Health & Fitness
Understanding Sustainable Public Health and Current Trends Shaping the Industry

The field of Public health is a dynamic setting that seeks to improve the health and well-being of populations through a variety of strategies, policies, and programs. With increasing global challenges such as climate change, pandemics, and health inequalities, the concept of “sustainable public health” has emerged as a crucial framework for addressing these issues in a holistic and long-term manner. This article provides an in-depth exploration of sustainable public health, examining its principles, current trends, and the evolving landscape of the industry.
What is Sustainable Public Health?
Sustainable public health is an approach that integrates principles of environmental sustainability, social equity, and economic viability to improve and protect population health over the long term. It is based on the understanding that human health is deeply interconnected with environmental and social factors. Therefore, sustainable public health aims to create systems and practices that not only address immediate health concerns but also promote long-term health benefits for current and future generations.
Key components of sustainable public health include:
- Environmental Sustainability: Ensuring that health practices and policies do not degrade natural resources or ecosystems. This involves promoting clean air, water, and safe food supplies, and addressing environmental hazards that can impact health.
- Social Equity: Addressing health disparities and ensuring that all populations have access to quality health care, education, and resources. Social equity in public health involves creating fair and just systems that prioritize vulnerable and marginalized communities.
- Economic Viability: Developing health systems and policies that are cost-effective and efficient. Economic viability ensures that public health interventions are financially sustainable and provide value for money.
The Importance of Sustainability in Public Health
The importance of sustainability in public health cannot be overstated. As global populations grow and urbanize, the strain on natural resources and health systems increases. Climate change, pollution, and resource depletion pose significant threats to health, necessitating a sustainable approach to address these challenges effectively.
Sustainable public health offers several key benefits:
- Long-Term Health Improvements: By focusing on sustainability, public health interventions can lead to lasting improvements in health outcomes, rather than short-term fixes that may not address underlying issues.
- Resilience to Emerging Threats: Sustainable practices help build resilience against emerging health threats, such as new infectious diseases or environmental disasters, by creating robust and adaptable health systems.
- Equitable Health Outcomes: Sustainable public health addresses social determinants of health and aims to reduce health disparities, promoting equitable access to resources and opportunities for all individuals.
Current Trends Shaping Sustainable Public Health
Climate Change and Health
One of the most pressing challenges for sustainable public health is climate change. The impact of climate change on health is profound and multifaceted, affecting air quality, water resources, and the prevalence of vector-borne diseases. The public health community is increasingly focused on understanding and mitigating these impacts.
Air Quality and Respiratory Health
Climate change contributes to worsening air quality through increased emissions of greenhouse gases and pollutants. Poor air quality is linked to a range of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, including asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and heart disease. Sustainable public health efforts are focused on reducing emissions, promoting clean energy, and advocating for policies that protect air quality.
Water Resources and Sanitation
Climate change also affects water availability and quality. Extreme weather events, such as floods and droughts, can contaminate water supplies and disrupt sanitation systems. Access to clean water and proper sanitation is essential for preventing waterborne diseases and promoting overall health. Sustainable public health initiatives work to improve water management, invest in resilient infrastructure, and ensure equitable access to clean water.
Vector-Borne Diseases
Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can alter the distribution of vector-borne diseases, such as malaria and dengue fever. Sustainable public health strategies involve monitoring disease patterns, developing early warning systems, and implementing vector control measures to prevent outbreaks.
Health Equity and Social Determinants of Health
Health equity is a central focus of sustainable public health, as it addresses the social determinants of health that contribute to disparities in health outcomes. These determinants include factors such as income, education, housing, and access to healthcare.
Addressing Health Disparities
Health disparities are differences in health outcomes between different population groups, often based on socioeconomic status, race, ethnicity, and geography. Sustainable public health seeks to reduce these disparities by addressing the root causes of inequality and ensuring that all individuals have access to the resources and opportunities necessary for good health.
Social Determinants of Health
Social determinants of health are the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age. These conditions influence health outcomes and are often shaped by policies and societal structures. Sustainable public health approaches work to improve these conditions through interventions that promote education, economic stability, and safe living environments.
Technology and Innovation in Public Health
Advancements in technology and innovation are transforming public health practices and creating new opportunities for sustainable solutions. These technologies range from digital health tools to new treatment modalities and data analytics.
Digital Health Tools
Digital health tools, such as mobile health apps, telemedicine, and electronic health records, are improving access to healthcare and enhancing patient engagement. These tools enable individuals to manage their health more effectively, reduce barriers to care, and promote preventive health practices.
Data Analytics and Predictive Modeling
Data analytics and predictive modeling are playing a crucial role in understanding and addressing public health issues. By analyzing large datasets, public health professionals can identify trends, predict outbreaks, and develop targeted interventions. This data-driven approach supports evidence-based decision-making and enhances the effectiveness of public health programs.
Innovative Treatments and Interventions
Technological innovations in treatments and interventions are advancing the field of public health. For example, new vaccines and therapies are being developed to address emerging infectious diseases, while innovative approaches to chronic disease management are improving health outcomes and quality of life for patients.
Sustainable Health Systems and Policies
Building sustainable health systems and policies is essential for achieving long-term health improvements and resilience. Sustainable health systems prioritize efficiency, accessibility, and equity, and are designed to adapt to changing needs and challenges.
Universal Health Coverage
Universal health coverage ensures that all individuals have access to essential health services without financial hardship. Sustainable health systems focus on expanding coverage, improving the quality of care, and reducing out-of-pocket costs for patients.
Integrated Health Services
Integrated health services aim to provide comprehensive and coordinated care across different levels of the health system. This approach promotes efficiency, reduces fragmentation, and improves patient outcomes by addressing both acute and chronic health needs in a holistic manner.
Policy and Advocacy
Policy and advocacy play a critical role in shaping sustainable public health. Advocates work to influence policies that promote health equity, environmental sustainability, and effective health systems. By engaging with policymakers and stakeholders, public health professionals can drive meaningful change and ensure that health policies are aligned with sustainable development goals.
Case Studies in Sustainable Public Health
Case Study 1: The Netherlands’ Climate and Health Strategy
The Netherlands has developed a comprehensive climate and health strategy that addresses the intersection of climate change and public health. The strategy includes measures to improve air quality, enhance water management, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. By integrating health considerations into climate policies, the Netherlands aims to protect public health while mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Case Study 2: The WHO’s Health and Equity Framework
The World Health Organization (WHO) has developed a Health and Equity Framework that focuses on addressing health disparities and promoting social determinants of health. The framework provides guidance on developing policies and programs that reduce inequalities and improve health outcomes for marginalized populations.
Case Study 3: Kenya’s Digital Health Innovation
Kenya has implemented several digital health innovations to improve healthcare access and delivery. For example, the M-TIBA platform allows individuals to manage their health financing through mobile phones, improving access to health services and promoting financial protection. This innovative approach supports sustainable health systems by enhancing accessibility and efficiency.
Future Directions in Sustainable Public Health
Embracing a One Health Approach
The One Health approach recognizes the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health. By addressing health issues at the interface of these domains, the One Health approach aims to prevent disease outbreaks, improve health outcomes, and promote sustainability.
Advancing Health Equity
Advancing health equity remains a top priority for sustainable public health. Efforts to reduce health disparities and address social determinants of health will continue to be essential in achieving equitable health outcomes and ensuring that all individuals have access to the resources they need to thrive.
Fostering Collaboration and Partnerships
Collaboration and partnerships are crucial for advancing sustainable public health. By working together with governments, organizations, communities, and individuals, public health professionals can leverage resources, share expertise, and drive innovative solutions to complex health challenges.
Investing in Education and Workforce Development
Investing in education and workforce development is essential for building a sustainable public health workforce. By providing training and professional development opportunities, public health organizations can ensure that their staff are equipped with the skills and knowledge needed to address evolving health challenges and drive progress in the field.
Conclusion
Sustainable public health is a comprehensive and forward-thinking approach that integrates environmental, social, and economic considerations to improve and protect population health. As global challenges such as climate change, health inequities, and emerging threats continue to evolve, sustainable public health practices will play a crucial role in shaping the future of health and well-being. By embracing innovative solutions, addressing social determinants of health, and fostering collaboration, the public health community can work towards a healthier, more equitable, and sustainable future for all.
-
 Press Release4 days ago
Press Release4 days agoClinical Trials Market Set for Robust Growth, Driven by Drug Development Surge and Digital Innovation
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoFill-Finish Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Market Expected to Flourish Amid Biopharmaceutical Boom and Global Outsourcing Trend by 2035
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoHow Managed IT Solutions Help Small Teams Compete at Enterprise Scale
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoGreen Bio Chemicals Market Poised for Sustainable Growth amidst Global Shift to Eco-Friendly Alternatives by 2035
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoIndustrial Boiler Market Expected to Surpass USD 24.4 Billion by 2035 Amid Growing Demand for Energy Efficiency and Industrialization
-
 Press Release5 days ago
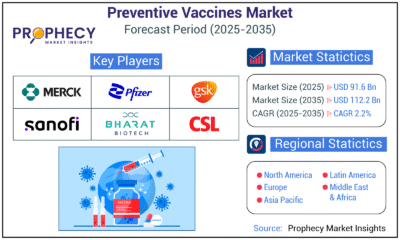
Press Release5 days agoPreventive Vaccines Market to Witness Strong Growth by 2035
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoPet Food Nutraceutical Market Set for Robust Expansion Amid Rising Demand for Pet Wellness by 2035
-

 Press Release4 days ago
Press Release4 days agoWaterproof Structural Adhesives Market: A Comprehensive Study Towards USD 10.3 Billion in 2035