Health & Fitness
LGBTQ+ Health Issues: Addressing Unique Healthcare Needs

The health and well-being of the LGBTQ+ (lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer/questioning, and other identities) community have gained significant attention over recent decades. This attention reflects a growing recognition of the unique healthcare needs and disparities faced by LGBTQ+ individuals. Despite progress, the community continues to encounter barriers to accessing healthcare, which can result in poorer health outcomes compared to the general population. This article delves into the various health issues affecting the LGBTQ+ community, the social and structural determinants of health, and the steps necessary to address these disparities.
Understanding the Unique Health Needs of LGBTQ+ Individuals
1. Physical Health Disparities
LGBTQ+ individuals experience distinct health disparities that stem from both biological factors and social determinants. Some of the critical physical health concerns include:
Sexual and Reproductive Health
- HIV/AIDS and STIs: Gay, bisexual men, and transgender women are disproportionately affected by HIV/AIDS and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). In the U.S., gay and bisexual men account for a substantial percentage of new HIV diagnoses each year. Lack of access to preventive measures like pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and limited awareness contribute to these statistics.
- Reproductive Health Needs: Lesbian and bisexual women may have different reproductive health needs and may not receive appropriate screening and counseling for contraception, pregnancy, and sexually transmitted diseases. The assumption of heterosexuality by healthcare providers often leads to inadequate care.
Chronic Diseases
- Cancer: Certain cancers have a higher prevalence among LGBTQ+ populations. For instance, lesbian and bisexual women may have a higher risk for breast cancer due to lower rates of childbirth and higher rates of obesity. Additionally, transgender individuals face challenges in accessing gender-affirming care, which can include cancer screening services.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Stress from discrimination and stigma has been linked to a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases among LGBTQ+ people. High rates of smoking, substance use, and physical inactivity in these communities further compound this risk.
2. Mental Health Disparities
The LGBTQ+ community faces higher rates of mental health disorders compared to the general population. This is often a result of minority stress — the chronic social stress experienced by marginalized groups.
Anxiety and Depression
LGBTQ+ individuals are more likely to experience anxiety and depression, which can be exacerbated by factors such as family rejection, discrimination, and violence. According to studies, the rates of depression and anxiety are significantly higher among LGBTQ+ youth, particularly those who experience rejection from their families.
Suicidal Behavior
The risk of suicidal behavior is notably higher in the LGBTQ+ community, especially among transgender individuals. Studies indicate that transgender people have an alarmingly high lifetime suicide attempt rate, often linked to experiences of gender dysphoria, societal stigma, and lack of access to supportive healthcare.
Substance Use Disorders
Substance use, including tobacco, alcohol, and illicit drugs, is more prevalent in the LGBTQ+ community. This higher prevalence is often a coping mechanism for dealing with discrimination, harassment, and social exclusion.
3. Barriers to Healthcare Access
LGBTQ+ individuals face numerous barriers to accessing healthcare, including:
Discrimination and Stigma
Discrimination in healthcare settings remains a significant barrier. Many LGBTQ+ individuals report having been refused care, subjected to harsh language, or discriminated against due to their sexual orientation or gender identity. This discrimination discourages many from seeking necessary medical care.
Lack of Provider Knowledge and Training
Healthcare providers often lack the training to address the unique needs of LGBTQ+ patients. This gap in knowledge can lead to inappropriate or inadequate care, and it often prevents individuals from seeking medical attention due to fear of being misunderstood or judged.
Financial Barriers
LGBTQ+ individuals are more likely to experience poverty and lack health insurance compared to their heterosexual and cisgender peers. This economic vulnerability makes it difficult for many to afford necessary healthcare services, including preventive care and mental health support.
Geographical Barriers
LGBTQ+ individuals living in rural areas often face additional challenges, such as limited access to LGBTQ+ friendly healthcare providers. The scarcity of specialized services forces many to travel long distances for appropriate care, further discouraging routine medical visits.
Addressing LGBTQ+ Health Disparities
To effectively address the health disparities faced by the LGBTQ+ community, a multifaceted approach is required, involving changes at the individual, healthcare provider, and systemic levels.
1. Improving Healthcare Provider Education and Training
One of the most critical steps in addressing LGBTQ+ health disparities is ensuring that healthcare providers are adequately trained. This training should encompass:
Cultural Competency
Healthcare professionals should receive training on the unique health needs of LGBTQ+ individuals and the social contexts affecting their health. Cultural competency training helps providers understand and address the specific health concerns of their LGBTQ+ patients, fostering a more inclusive and supportive healthcare environment.
Gender-Affirming Care
For transgender and gender non-conforming individuals, receiving gender-affirming care can significantly improve mental and physical health outcomes. Providers should be trained to offer appropriate hormone therapy, surgical options, and mental health support, as well as routine care tailored to the needs of transgender patients.
2. Expanding Access to LGBTQ+ Inclusive Healthcare Services
Ensuring that LGBTQ+ individuals have access to inclusive and affirming healthcare is crucial. This can be achieved by:
Creating LGBTQ+ Friendly Clinics and Services
Developing healthcare facilities that specialize in LGBTQ+ health, or at least have dedicated services for LGBTQ+ patients, can help reduce the barriers to accessing care. These clinics should be staffed with providers who are trained in LGBTQ+ health issues and can offer a welcoming environment.
Telemedicine Services
Telemedicine can be an effective way to provide care to LGBTQ+ individuals, particularly those in rural or underserved areas. It allows patients to connect with providers who have expertise in LGBTQ+ health, reducing the need to travel and the associated financial burden.
3. Policy and Legal Reforms
Legal and policy changes are essential to reducing health disparities and protecting the rights of LGBTQ+ individuals. Key reforms include:
Anti-Discrimination Protections
Implementing and enforcing anti-discrimination laws in healthcare is critical. Such policies ensure that LGBTQ+ individuals cannot be denied care or treated unfairly based on their sexual orientation or gender identity.
Health Insurance Reforms
Reforming health insurance policies to cover LGBTQ+ specific healthcare needs, such as hormone therapy, gender-affirming surgeries, and fertility treatments, is essential. Insurance providers should not exclude these services from coverage, as they are crucial for the health and well-being of LGBTQ+ individuals.
4. Community Support and Advocacy
Community-based organizations play a vital role in supporting the health of LGBTQ+ individuals. These organizations can:
Provide Social Support
Peer support groups and community organizations provide safe spaces for LGBTQ+ individuals to share experiences and access resources. Such support is particularly important for mental health and can reduce feelings of isolation and distress.
Advocate for Change
LGBTQ+ advocacy organizations work to raise awareness of health disparities and push for changes in healthcare policies and practices. Their efforts are crucial in shaping a more inclusive and equitable healthcare system.
The Role of Research in LGBTQ+ Health
Research is fundamental to understanding and addressing the health needs of the LGBTQ+ community. However, LGBTQ+ health research has historically been underfunded and understudied. To effectively address health disparities, it is essential to:
Increase Funding for LGBTQ+ Health Research
Increased funding is necessary to support research on the unique health needs of LGBTQ+ individuals. This includes studies on the prevalence of health conditions, the effectiveness of different interventions, and the impact of social determinants on health outcomes.
Encourage Community-Based Participatory Research
Community-based participatory research (CBPR) involves collaboration between researchers and community members. This approach ensures that research is relevant to the community’s needs and that the findings are used to improve health outcomes.
Expand Data Collection on Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity
Collecting data on sexual orientation and gender identity in health surveys and medical records is essential for understanding the health needs of the LGBTQ+ community. This data helps identify health disparities and informs the development of targeted interventions.
Conclusion
The health issues faced by the LGBTQ+ community are complex and multifaceted, requiring a comprehensive and inclusive approach. Addressing these issues involves improving healthcare provider education, expanding access to inclusive services, enacting supportive policies, and fostering community support. Research plays a crucial role in understanding and addressing these disparities.
Ultimately, creating a healthcare system that meets the unique needs of LGBTQ+ individuals is not only a matter of equity but also a public health imperative. By ensuring that LGBTQ+ individuals receive the care they need and deserve, we can improve the health and well-being of this diverse and vibrant community.
-

 Press Release3 days ago
Press Release3 days agoNura Labs Files Revolutionary Patent: AI-Powered Wallet Solves the $180 Billion Crypto Staking Complexity Crisis
-
 Press Release1 day ago
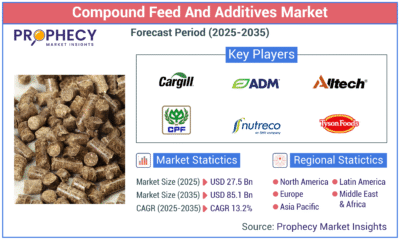
Press Release1 day agoGlobal Compound Feeds and Additives Industry Report: Market Expansion and Competitive Insights to 2035
-

 Technology1 day ago
Technology1 day agoWhat to Know Before Switching Cell Phone Network Services in 2025