Public Safety
Genetic Disorders: How to Manage and Plan for the Future

Genetic disorders represent a complex intersection of biology, medicine, and personal experience. They arise from mutations or alterations in an individual’s DNA, which can manifest in a myriad of ways, ranging from mild conditions to life-threatening diseases. Understanding these disorders, their implications, and the strategies for management is crucial for affected individuals and families. This article delves into the nature of genetic disorders, their classification, management strategies, and how to plan for a future impacted by genetic conditions.
Understanding Genetic Disorders
Genetic disorders can be broadly classified into three categories: single-gene disorders, chromosomal disorders, and multifactorial disorders.
Single-Gene Disorders
Mutations in one particular gene cause single-gene disorders. These can be inherited in a Mendelian fashion, which includes:
Autosomal Dominant Disorders: Only one copy of the mutated gene from an affected parent can cause the disorder. Examples include Huntington’s disease and Marfan syndrome.
Autosomal Recessive Disorders: Two copies of the mutated gene (one from each parent) are required for the individual to be affected. Cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anemia are prominent examples.
X-Linked Disorders: These disorders are linked to genes on the X chromosome and are more commonly expressed in males, who have only one X chromosome. Hemophilia and Duchenne muscular dystrophy fall under this category.
Chromosomal Disorders
Chromosomal disorders arise from changes in the number or structure of chromosomes. This can include conditions such as Down syndrome, which results from an extra copy of chromosome 21 (trisomy 21), or Turner syndrome, which occurs in females with a missing or incomplete X chromosome.
Multifactorial Disorders
Multifactorial disorders result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers may have a genetic predisposition but also depend on lifestyle and environmental influences.
Impact of Genetic Disorders
The impact of genetic disorders extends beyond physical health; they also affect psychological, social, and financial aspects of life. Individuals and families often face emotional challenges, including anxiety and depression. Additionally, navigating healthcare systems, understanding insurance coverage, and managing care can lead to significant financial strain.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
The emotional toll of genetic disorders is profound. Parents receiving a diagnosis for their child may experience grief, guilt, and fear. Individuals with genetic conditions may struggle with self-esteem and identity, particularly in cases of visible disabilities or chronic illnesses.
Social Implications
Social stigma can compound the challenges faced by individuals with genetic disorders. Misunderstandings about conditions often lead to isolation and discrimination. Support networks, including family, friends, and community resources, are essential for fostering social connections and resilience.
Financial Considerations
The financial implications of managing genetic disorders can be overwhelming. Costs associated with medical treatments, therapies, special education, and long-term care can accumulate rapidly. Health insurance coverage varies, and families may need to advocate for necessary services and support.
Management Strategies
Managing genetic disorders requires a multi-faceted approach that encompasses medical care, psychological support, and lifestyle adaptations.
Medical Management
Early Diagnosis and Intervention: Early detection through genetic testing and screenings is crucial. Many disorders can benefit from early interventions, improving quality of life and outcomes.
Regular Monitoring: Individuals with genetic conditions often require regular check-ups and monitoring to manage symptoms and complications. This proactive approach helps in adjusting treatment plans as needed.
Therapeutic Approaches: Depending on the condition, various therapies may be employed. These can include medication, physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy. In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary.
Genetic Counseling: Genetic counselors play a vital role in helping families understand genetic disorders. They provide information about inheritance patterns, risks for future pregnancies, and available testing options. Counseling can also support emotional needs by addressing concerns and expectations.
Psychological Support
Counseling and Therapy: Professional psychological support can help individuals and families cope with the emotional challenges associated with genetic disorders. Therapists specializing in chronic illness can provide strategies for resilience and coping.
Support Groups: Joining support groups can connect individuals and families with others facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences and advice fosters community and reduces feelings of isolation.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Healthy Living: Emphasizing a healthy lifestyle can significantly impact overall well-being. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep are vital components in managing health.
Education and Advocacy: Educating oneself about the specific genetic disorder can empower individuals and families. Advocacy for necessary accommodations in schools and workplaces can improve access and quality of life.
Planning for the Future
Planning for the future when dealing with genetic disorders involves foresight, preparation, and resilience. Here are several key considerations:
Family Planning
Genetic Testing: Couples with a family history of genetic disorders may choose to undergo genetic testing to assess risks for their children. Understanding carrier status can inform family planning decisions.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) with Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD): For couples at high risk of passing on genetic disorders, IVF combined with PGD allows for the selection of embryos free from specific genetic conditions.
Adoption and Surrogacy: Exploring alternative family-building options, such as adoption or surrogacy, can be fulfilling paths for those concerned about hereditary conditions.
Financial Planning
Insurance Coverage: Understanding health insurance policies and potential coverage for treatments is critical. Families should explore all options, including government assistance programs.
Special Needs Trusts: Establishing a special needs trust can provide financial support for individuals with disabilities while preserving eligibility for government benefits.
Long-Term Care Plans: Considering future care needs and creating a long-term care plan ensures that individuals with genetic disorders receive appropriate support as they age.
Advocacy and Awareness
Community Engagement: Becoming involved in advocacy organizations can provide support and resources. These organizations often work towards raising awareness, funding research, and providing education on genetic disorders.
Education for Others: Raising awareness within the community helps combat stigma and promotes understanding of genetic disorders. Sharing personal stories can foster empathy and support.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of genetic disorders requires a comprehensive understanding of the conditions, effective management strategies, and thoughtful planning for the future. The emotional, social, and financial implications can be profound, yet with proper support and resources, individuals and families can lead fulfilling lives.
As our understanding of genetics continues to evolve, advancements in research, technology, and therapies promise new possibilities for those affected by genetic disorders. Embracing a proactive approach, prioritizing mental and emotional health, and fostering community connections will empower individuals and families to navigate their unique journeys with resilience and hope.
-

 Press Release6 days ago
Press Release6 days agoBellarium ($BEL) Price Prediction: Could It Hit $5 by 2026?
-
 Press Release3 days ago
Press Release3 days agoClinical Trials Market Set for Robust Growth, Driven by Drug Development Surge and Digital Innovation
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoHow Managed IT Solutions Help Small Teams Compete at Enterprise Scale
-

 Press Release4 days ago
Press Release4 days agoFill-Finish Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Market Expected to Flourish Amid Biopharmaceutical Boom and Global Outsourcing Trend by 2035
-

 Press Release4 days ago
Press Release4 days agoIndustrial Boiler Market Expected to Surpass USD 24.4 Billion by 2035 Amid Growing Demand for Energy Efficiency and Industrialization
-
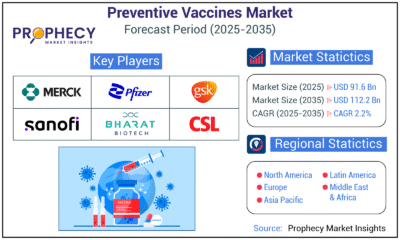
 Press Release4 days ago
Press Release4 days agoPreventive Vaccines Market to Witness Strong Growth by 2035
-

 Press Release4 days ago
Press Release4 days agoGreen Bio Chemicals Market Poised for Sustainable Growth amidst Global Shift to Eco-Friendly Alternatives by 2035
-

 Press Release4 days ago
Press Release4 days agoPet Food Nutraceutical Market Set for Robust Expansion Amid Rising Demand for Pet Wellness by 2035