Health & Fitness
COVID-19 Vaccines: Ongoing Updates on Variants, Booster Shots, and Vaccine Efficacy
As we approach the latter half of 2024, the landscape of COVID-19 and its mitigation strategies, particularly vaccination, continues to evolve. With the emergence of new variants and the corresponding updates to vaccines, understanding the current state of COVID-19 prevention is critical for public health.
Current Variants and Their Impact
The SARS-CoV-2 virus, responsible for COVID-19, continues to mutate, leading to the emergence of new variants that challenge the effectiveness of existing vaccines. The dominant variants as of mid-2024 are KP.2 and KP.3, both of which belong to a lineage known as FLiRT variants. These are subvariants of the JN.1 strain, which itself is a descendant of the Omicron variant first identified in late 2021.
The FLiRT variants have shown a significant ability to escape immune protection, evading antibodies generated from previous infections and vaccinations. Specifically, these variants have demonstrated a five- to tenfold increase in immune evasion compared to the XBB variant, which was prevalent during the last booster campaign. Despite these challenges, the current understanding is that the mutations in these variants, while notable, are not sufficient to completely evade immunity, particularly in individuals with prior exposure to the virus or vaccination. This ongoing evolution underscores the importance of updating vaccines to maintain their effectiveness.
Updated Vaccines for 2024-2025
In response to the evolving variants, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved new formulations of the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines for the 2024-2025 season. These updated vaccines, produced by Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech, specifically target the KP.2 strain, a subvariant within the JN.1 lineage. The decision to update the vaccines was driven by data showing waning immunity from earlier vaccine formulations and the need for better protection against the currently circulating strains.
The new vaccines are monovalent, focusing solely on the KP.2 strain, which is expected to be dominant in the upcoming fall and winter seasons. The FDA and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have recommended these updated vaccines for all eligible individuals, particularly emphasizing the importance of vaccination for those at higher risk of severe outcomes, including older adults and individuals with underlying health conditions.
Booster Shots and Waning Immunity
Booster shots have become a critical component in maintaining immunity against COVID-19, particularly as studies continue to show that the protection offered by initial vaccinations wanes over time. The latest data indicates that vaccine-induced immunity peaks about four weeks after vaccination but then gradually decreases. This decline in immunity has led to an increase in COVID-19 cases, especially during periods of heightened virus transmission, such as the summer of 2024.
Booster shots, particularly those updated to target specific variants, have been shown to restore and even enhance immunity. For instance, individuals who received the 2023-2024 booster shot, which was designed to combat the XBB variant, experienced significantly reduced rates of illness and hospitalization compared to those who did not receive the booster. This pattern is expected to continue with the 2024-2025 booster, which is specifically formulated to address the challenges posed by the KP.2 strain.
Efficacy and Safety of Current Vaccines
The efficacy of the updated vaccines is closely monitored through various studies and real-world data. As of the latest reports, the new monovalent vaccines are expected to offer robust protection against the currently circulating variants. However, their effectiveness, particularly in preventing mild to moderate infections, may still vary depending on individual factors such as age, underlying health conditions, and previous exposure to the virus.
Despite these challenges, the updated vaccines are anticipated to significantly reduce the risk of severe disease, hospitalization, and death, much like their predecessors. Moreover, the safety profile of these vaccines remains strong. The FDA continues to affirm that the benefits of COVID-19 vaccination far outweigh the risks, with adverse events remaining rare and generally mild.
Looking Ahead: Annual COVID-19 Vaccination?
Given the constant evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, there is an increasing likelihood that COVID-19 vaccines may become an annual necessity, similar to influenza vaccines. The FDA has indicated that unless a drastically different variant emerges, the composition of COVID-19 vaccines will be reviewed and updated annually, reflecting the most current strains of the virus.
This approach aims to simplify the vaccination process and ensure that the population remains protected against the most relevant variants each year. The integration of COVID-19 vaccines into the annual vaccine schedule would represent a significant shift in public health strategy, emphasizing the importance of ongoing vigilance and adaptation in the face of a persistent viral threat.
Global Implications and Equity in Vaccine Distribution
As high-income countries update their vaccination strategies, there remains a significant disparity in vaccine access and uptake globally. While the updated mRNA vaccines are readily available in countries like the United States, many low- and middle-income countries continue to rely on older vaccine formulations, such as the AstraZeneca vaccine or inactivated virus vaccines like Sinopharm and Sinovac. These vaccines, while still effective, may not offer the same level of protection against newer variants.
Efforts to ensure equitable distribution of updated vaccines are ongoing but face numerous challenges, including production limitations, logistical hurdles, and geopolitical factors. The World Health Organization (WHO) and other international bodies continue to advocate for global vaccine equity, emphasizing that the pandemic cannot truly end until all countries have access to effective and up-to-date vaccines.
Conclusion
The ongoing evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 virus necessitates a dynamic response in vaccine development and distribution. The updated 2024-2025 COVID-19 vaccines represent the latest effort to keep pace with the virus’s mutations, offering renewed hope for controlling the pandemic’s impact. However, the success of these vaccines depends not only on their scientific efficacy but also on their widespread acceptance and equitable distribution across the globe. As the world continues to navigate this complex public health challenge, staying informed and adapting to new developments remains crucial for both individuals and communities.
-
 Press Release4 days ago
Press Release4 days agoClinical Trials Market Set for Robust Growth, Driven by Drug Development Surge and Digital Innovation
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoFill-Finish Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Market Expected to Flourish Amid Biopharmaceutical Boom and Global Outsourcing Trend by 2035
-

 Press Release7 days ago
Press Release7 days agoBellarium ($BEL) Price Prediction: Could It Hit $5 by 2026?
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoHow Managed IT Solutions Help Small Teams Compete at Enterprise Scale
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoGreen Bio Chemicals Market Poised for Sustainable Growth amidst Global Shift to Eco-Friendly Alternatives by 2035
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoIndustrial Boiler Market Expected to Surpass USD 24.4 Billion by 2035 Amid Growing Demand for Energy Efficiency and Industrialization
-
 Press Release5 days ago
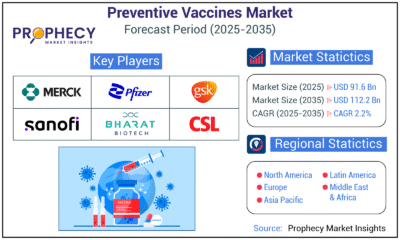
Press Release5 days agoPreventive Vaccines Market to Witness Strong Growth by 2035
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoPet Food Nutraceutical Market Set for Robust Expansion Amid Rising Demand for Pet Wellness by 2035