Alternative Energy
Biomanufacturing Innovation: Pioneering the Future of Production

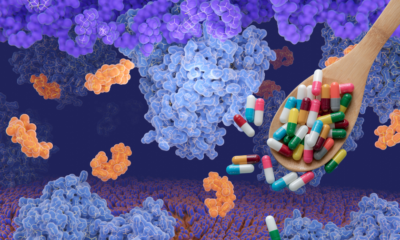
Biomanufacturing innovation is reshaping the future of production by integrating advanced technologies and biological processes. This article explores how these innovations are transforming various sectors, enhancing sustainability, and addressing global challenges. From nanotechnology to biomanufacturing in the pharmaceutical industry, the future of production is becoming increasingly efficient and environmentally friendly.
Key Takeaways
- Nanotechnology is changing materials and coatings, making products stronger and lighter.
- Biomanufacturing uses living organisms to create sustainable products, reducing environmental impact.
- The pharmaceutical industry is leveraging biomanufacturing for advanced therapies, but faces challenges in scaling production.
- Precision fermentation is revolutionising food production, making it more efficient and sustainable.
- Continuous production methods are enhancing efficiency in biomanufacturing, allowing for quicker and more reliable output.
The Role of Nanotechnology in Biomanufacturing Innovation
Nanotechnology is changing the way we think about manufacturing. By working with materials at a tiny scale, manufacturers can create products that are stronger, lighter, and more efficient. This technology is set to transform various sectors of manufacturing.
Revolutionising Materials and Coatings
- Stronger Materials: Nanotechnology allows for the creation of materials that are much tougher than traditional ones.
- Advanced Coatings: These coatings can make surfaces more resistant to wear and tear, improving product lifespan.
- Smart Materials: Some materials can change properties in response to environmental conditions, offering new functionalities.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency
Nanotechnology plays a crucial role in improving energy efficiency. For example:
- High-Performance Batteries: Nanomaterials can enhance battery capacity and charging speed.
- Solar Cells: Nanotechnology can increase the efficiency of solar panels, making renewable energy more accessible.
- Insulation: Improved insulation materials can reduce energy consumption in buildings.
Impact on Various Manufacturing Sectors
The influence of nanotechnology extends across multiple sectors:
- Pharmaceuticals: Targeted drug delivery systems can be developed using nanoparticles.
- Food Industry: Nanotechnology can improve food packaging, extending shelf life and safety.
- Textiles: Fabrics can be made more durable and stain-resistant through nanotechnology.
Nanotechnology is not just a trend; it is a fundamental shift in how we produce and use materials, paving the way for a more sustainable future.
Harnessing Biological Processes for Sustainable Production

Utilising Living Organisms
Biomanufacturing uses living organisms to create products that are more sustainable. This method can replace traditional processes that rely on fossil fuels. By using microbes and enzymes, we can produce a variety of materials, including:
- Bio-based chemicals
- Enzymes for food processing
- Vitamins and amino acids
Environmental Benefits
The shift to biomanufacturing offers several environmental advantages:
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
- Minimises waste by using renewable resources.
- Supports biodiversity by decreasing reliance on animal-derived ingredients.
Reducing Resource-Intensive Processes
Biomanufacturing can significantly lower the use of resources in production. This is achieved by:
- Optimising fermentation processes to increase yield.
- Using genetic engineering to enhance product quality.
- Implementing continuous production methods to improve efficiency.
By harnessing bio-based chemicals and enzymes for a sustainable substitute for conventional chemicals, we can create a more eco-friendly future.
In summary, biomanufacturing not only helps in producing essential goods but also plays a crucial role in protecting our environment and promoting sustainability.
Biomanufacturing in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Production of Biopharmaceuticals
Biomanufacturing is crucial in the pharmaceutical sector, as it enables the production of vital medicines. This process uses living organisms to create drugs, which can lead to more effective treatments. Some key products include:
- Insulin for diabetes management
- Monoclonal antibodies for various diseases
- Vaccines for infectious diseases
Advancements in Cell and Gene Therapies
Recent innovations in biomanufacturing have paved the way for cell and gene therapies. These therapies offer new hope for treating genetic disorders and cancers. Notable advancements include:
- CRISPR technology for gene editing
- CAR-T cell therapy for cancer treatment
- Stem cell therapies for regenerative medicine
Challenges and Opportunities
While biomanufacturing holds great promise, it also faces challenges. Some of these include:
- High production costs
- Regulatory hurdles
- Need for skilled workforce
However, the opportunities are vast, especially in addressing global health needs.
Biomanufacturing is not just about producing drugs; it’s about educating and diversifying the future of biomanufacturing, ensuring that we meet the healthcare demands of tomorrow.
Precision Fermentation: A New Era in Food Production

Historical Context and Evolution
Precision Fermentation (PF) is a groundbreaking method that uses microorganisms to create food ingredients. This technology is changing how we produce food. It started in the 1980s with cheese production, where E. coli was used to make chymosin, a key ingredient in cheese-making. This innovation has since expanded to various food products, making it a vital part of modern food production.
Applications in Food Ingredients
PF has numerous applications in the food industry, including:
- Dairy alternatives: Producing proteins without using animals.
- Plant-based ingredients: Creating flavours and textures that mimic traditional foods.
- Nutritional supplements: Enhancing food with essential nutrients.
| Application | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Dairy Alternatives | Non-animal derived proteins | Vegan cheese |
| Plant-based Ingredients | Flavours and textures for meat substitutes | Plant-based burgers |
| Nutritional Supplements | Added vitamins and minerals | Fortified foods |
Future Prospects
The future of PF looks promising. As technology advances, we can expect:
- Increased efficiency: More effective production methods.
- Wider adoption: More companies using PF in their products.
- Sustainability: Reduced environmental impact from food production.
The shift towards Precision Fermentation is not just a trend; it is a necessary evolution in how we think about food production and sustainability.
By embracing PF, we can create a more sustainable food system that meets the needs of a growing population while reducing our reliance on traditional animal farming.
Continuous Production: Enhancing Efficiency in Biomanufacturing
Understanding Continuous Production
Continuous production is a method that allows for the ongoing creation of products without the interruptions typical of batch processes. This approach can significantly improve productivity and reduce waste, making it a vital part of modern biomanufacturing.
Key Benefits and Innovations
The advantages of continuous production include:
- Efficiency: Minimises downtime and maximises output.
- Scalability: Easily adjusts to meet changing production needs.
- Innovation: Facilitates the integration of new technologies.
- Resiliency: Fresh media reduces toxicity, promoting healthier cell growth.
- Immediacy: Continuous harvesting of cells and molecules of interest.
Overcoming Industry Hurdles
While the benefits are clear, there are challenges to implementing continuous production. These include:
- Technical limitations in current equipment.
- Regulatory hurdles that need addressing.
- The need for industry-wide standards to ensure consistency.
Continuous production is not just a trend; it is becoming a cornerstone technology for the future of biomanufacturing. By transitioning from batch to continuous processes, companies can enhance productivity and reduce environmental impacts.
In summary, continuous production represents a significant leap forward in biomanufacturing, offering numerous benefits while also presenting challenges that the industry must work to overcome.
Scaling Up: From Lab to Commercial Biomanufacturing
Challenges in Scaling Production
Scaling biomanufacturing from a laboratory setting to commercial production involves several challenges:
- Variability in Biological Processes: Biological systems can be unpredictable, making it hard to replicate results.
- Infrastructure Needs: Upgrading facilities to handle larger volumes is essential.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting industry standards can be complex and time-consuming.
Infrastructure and Workforce Needs
To successfully scale up, companies must consider:
- Investment in Equipment: Upgrading to larger bioreactors and automation systems.
- Skilled Workforce: Hiring and training staff with expertise in biomanufacturing processes.
- Quality Control Systems: Implementing robust systems to ensure product consistency and safety.
Strategies for Successful Scale-Up
To navigate the scaling process effectively, companies can adopt the following strategies:
- Pilot Projects: Conducting small-scale trials to validate processes before full-scale production.
- Collaboration: Partnering with research institutions and industry leaders to share knowledge and resources.
- Techno-Economic Analysis: Evaluating the cost-effectiveness of production methods to ensure profitability.
Scaling up biomanufacturing is not just about increasing volume; it’s about ensuring that processes remain efficient and sustainable. Capabilities in US national laboratories can help ensure scale-up and translational feasibility of new and emerging biomanufacturing processes.
Biomanufacturing and the Future of the Bioeconomy
Transforming Economic Sectors
Biomanufacturing is set to change many parts of the economy. It can create more sustainable products and help meet climate goals. This shift is crucial for building a stronger bioeconomy. Here are some key areas where biomanufacturing is making a difference:
- Pharmaceuticals: Producing medicines more efficiently.
- Food Production: Creating healthier food options.
- Materials: Developing biodegradable plastics.
Meeting Climate Goals
The role of biomanufacturing in achieving climate targets is significant. By using biological processes, we can:
- Reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Replace harmful materials with sustainable alternatives.
- Improve energy efficiency in production.
Building Resilient Supply Chains
A strong bioeconomy relies on robust supply chains. Biomanufacturing helps create these by:
- Encouraging local production to reduce transport emissions.
- Supporting diverse sources of materials to avoid shortages.
- Fostering partnerships between industries and research institutions.
Biomanufacturing is not just about making products; it’s about creating a sustainable future for our planet.
In summary, biomanufacturing is a key player in shaping the future of the bioeconomy, driving innovation, and promoting sustainability across various sectors. It is essential for meeting both economic and environmental goals, ensuring a healthier planet for future generations.
Innovative Applications of Biomanufacturing
Pharmaceuticals and Vaccines
Biomanufacturing is crucial in the production of pharmaceuticals and vaccines. By using living organisms, we can create complex drugs more efficiently. This method allows for:
- Higher precision in drug formulation.
- Reduced costs compared to traditional methods.
- Faster production times, which is vital during health crises.
Textiles and Cosmeceuticals
In the textile industry, biomanufacturing is changing the game. It enables the creation of sustainable fabrics and materials. Some benefits include:
- Eco-friendly production processes.
- Use of biodegradable materials.
- Development of innovative dyes and finishes that are less harmful to the environment.
Fuel Enzymes and Beyond
Biomanufacturing also plays a significant role in producing enzymes for biofuels. These enzymes help break down materials into usable energy sources. Key points include:
- Sustainable energy production.
- Reduction of reliance on fossil fuels.
- Potential for lower emissions during production.
Biomanufacturing is not just about efficiency; it’s about creating a more sustainable future for all industries. Innovative applications are paving the way for a greener planet.
The Global Impact of Biomanufacturing Innovation
Regional Case Studies
Biomanufacturing is making waves across the globe, with various regions showcasing its potential:
- North America: Leading in biopharmaceuticals, with significant investments in cell and gene therapies.
- Europe: Focused on sustainable practises, integrating biomanufacturing into traditional industries.
- Asia: Rapidly expanding in bioplastics and biofuels, driven by government support and innovation.
International Collaborations
Collaboration is key to advancing biomanufacturing:
- Public-Private Partnerships: Governments and companies working together to fund research.
- Academic Collaborations: Universities partnering with industries to develop new technologies.
- Global Networks: Sharing knowledge and resources across borders to tackle common challenges.
Future Trends and Predictions
The future of biomanufacturing looks promising:
- Increased Investment: More funding for research and development.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in precision fermentation and synthetic biology.
- Sustainability Focus: A shift towards eco-friendly practises in production.
Biomanufacturing is accelerating the global transition to a bio-based economy, providing rapid responses to health crises and solutions to agricultural challenges caused by climate change.
The Intersection of Biotechnology and Manufacturing
Historical Development
The relationship between biotechnology and manufacturing has evolved significantly over the years. Initially, manufacturing relied heavily on traditional methods, but the introduction of biotechnology has transformed production processes. This shift has led to:
- Enhanced efficiency in production
- Development of sustainable practises
- Creation of innovative products that were previously unimaginable
Current Technological Trends
Today, several technological trends are shaping the intersection of biotechnology and manufacturing:
- Precision fermentation: This method uses microorganisms to produce high-value compounds, revolutionising food and pharmaceutical production.
- Synthetic biology: By redesigning organisms for specific purposes, manufacturers can create tailored solutions for various industries.
- Digital twins: This technology allows for real-time monitoring and optimisation of manufacturing processes, improving overall efficiency.
| Technology | Description | Impact on Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Precision Fermentation | Uses microbes for production | Increases yield and reduces waste |
| Synthetic Biology | Redesigns organisms for specific tasks | Enables custom solutions |
| Digital Twins | Virtual replicas for monitoring | Enhances efficiency and reduces costs |
Future Directions
Looking ahead, the integration of biotechnology into manufacturing is expected to grow. Key areas to watch include:
- Sustainable practises: Continued focus on reducing environmental impact.
- Collaboration: Increased partnerships between biotech firms and traditional manufacturers.
- Innovation: Ongoing development of new biotechnological methods to enhance production.
The fusion of biotechnology and manufacturing is not just a trend; it is a revolution that promises to reshape industries and create a more sustainable future.
Conclusion
In summary, biomanufacturing stands at the forefront of a new era in production. By using living organisms, this innovative approach not only enhances the efficiency of creating essential products but also promotes sustainability. As we look ahead, the potential for biomanufacturing to reshape various industries is immense. It offers solutions that are kinder to our planet while meeting the growing demands of society. With ongoing advancements and collaborations, the future of biomanufacturing promises to be bright, paving the way for a more sustainable and efficient world.
-

 Food14 hours ago
Food14 hours agoHow to Lose Weight Fast: The Best Drink Recipes for Rapid Results
-

 News7 hours ago
News7 hours agoUnfiltered: Behind the Headlines with Page Six
-

 Education14 hours ago
Education14 hours agoUnlocking the ASUS Student Discount on Reddit: A Comprehensive Guide
-

 Banking11 hours ago
Banking11 hours agoUnlock Your Financial Potential with SoFi High-Yield Savings