Medical
What are symptoms of being anemic?
anemia disease
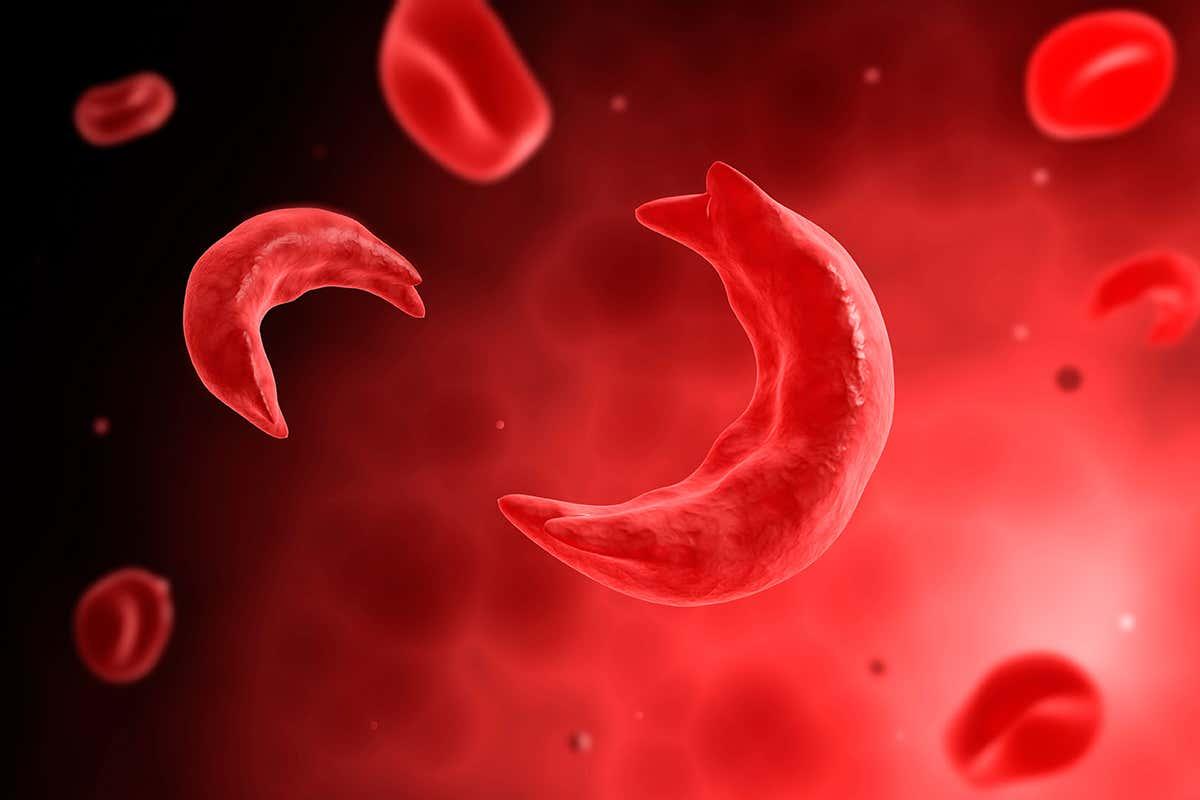
Anemia is defined as a low number of red blood cells. In a routine blood test, anemia is reported as low hemoglobin or hematocrit. Hemoglobin is the main protein in your red blood cells. It carries oxygen and delivers it throughout your body. If you have anemia, your hemoglobin level will be low too. If it is low enough, your tissues or organs may not get enough oxygen. Symptoms of anemia — like fatigue or shortness of breath — happen because your organs aren’t getting what they need to work the way they should.
Anemia is the most common blood condition in the U.S. It affects almost 6% of the population. Women, young children, and people with long-term diseases are more likely to have anemia. Important things to remember are:
Certain forms of anemia are passed down through your genes, and infants may have it from birth.
Women are at risk of iron deficiency anemia because of blood loss from their periods and higher blood supply demands during pregnancy.
Older adults have a greater risk of anemia because they Aplastic anemia causes in Pakistan are more likely to have kidney disease or other chronic medical conditions.
There are many types of anemia. All have different causes and treatments. Some forms — like the mild anemia that happens during pregnancy — aren’t a major concern. But some types of anemia maymay reflect a serious underlying medical condition.
Anemia Symptoms
The signs of anemia can be so mild that you might not even notice them. At a certain point, as your blood cells decrease, symptoms often develop. Depending on the cause of the anemia, symptoms may include:
Dizziness, lightheadedness, or feeling like you are about to pass out
Fast or unusual heartbeat
Headache
Pain, including in your bones, chest, belly, and joints
Problems with growth for children and teens
Shortness of breath
Skin that’s pale or yellow
Cold hands and feet
Tiredness or weakness
Anemia Types and Causes
There are more than 400 types of anemia, and they’re divided into three groups:
Anemia caused by blood loss
Anemia caused by decreased or faulty red blood cell production
Anemia caused by the destruction of red blood cells
Anemia Caused by Blood Loss
You can lose red blood cells through bleeding. This can happen slowly over a long period, and you might not notice. Causes can include:
Gastrointestinal conditions such as ulcers, hemorrhoids, gastritis (inflammation of your stomach), and cancer
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin or ibuprofen, which can cause ulcers and gastritis
A woman’s period, especially if you have heavy menstruation (or heavy period). This can be associated with fibroids.
Post-trauma or post-surgery as well.
Anemia Caused by Decreased or Faulty Red Blood Cell Production
With this type of anemia, your body may not create enough blood cells, or they may not work the way they should. This can happen because there’s something wrong with your red blood cells or because you don’t have enough minerals and vitamins for your red blood cells to form normally. Conditions associated with these causes of anemia include:
Bone marrow and stem cell problems
Iron-deficiency anemia
Sickle cell anemia
Vitamin-deficiency anemia, specifically b12 or folate
What organs are affected by anemia?
Bone marrow and stem cell problems may keep your body from producing enough red blood cells. Some of the stem cells in the marrow in the center of your bones will develop into red blood cells. If there aren’t enough stem cells, if they don’t work right, or if they’re replaced by other cells such as cancer cells, you might get anemia. Anemia caused by bone marrow or stem cell problems includes:
Aplastic anemia happens when you don’t have enough stem cells or have none at all. You might get aplastic anemia because of your genes or because your bone marrow was injured by medications, radiation, chemotherapy, or infection. Other malignancies that commonly affect the bone marrow include multiple myeloma or leukemia. Sometimes, there’s no clear cause of aplastic anemia.
Lead poisoning. Lead is toxic to your bone marrow, causing you to have fewer red blood cells. Lead poisoning can happen when adults contact information at work, for example, or if children eat chips of lead paint. You can also get it if your food comes into contact with some types of pottery that aren’t glazed right.
Conclusion
Thalassemia happens with a problem with hemoglobin formation (4 chains aren’t correctly formed). You make small red blood cells-though you can make enough of them to be asymptomatic, or it can be severe. It’s passed down in your genes and usually affects people of Mediterranean, African, Middle Eastern, and Southeast Asian descent. This condition can range from mild to life-threatening; the most severe form is called Cooley’s anemia.
-
 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoClinical Trials Market Set for Robust Growth, Driven by Drug Development Surge and Digital Innovation
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoGreen Bio Chemicals Market Poised for Sustainable Growth amidst Global Shift to Eco-Friendly Alternatives by 2035
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoFill-Finish Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Market Expected to Flourish Amid Biopharmaceutical Boom and Global Outsourcing Trend by 2035
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoIndustrial Boiler Market Expected to Surpass USD 24.4 Billion by 2035 Amid Growing Demand for Energy Efficiency and Industrialization
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoHow Managed IT Solutions Help Small Teams Compete at Enterprise Scale
-
 Press Release5 days ago
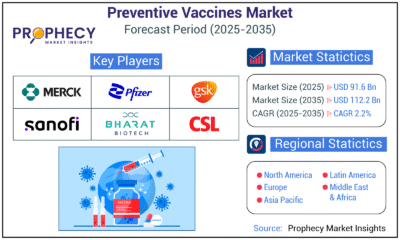
Press Release5 days agoPreventive Vaccines Market to Witness Strong Growth by 2035
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoPet Food Nutraceutical Market Set for Robust Expansion Amid Rising Demand for Pet Wellness by 2035
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoWaterproof Structural Adhesives Market: A Comprehensive Study Towards USD 10.3 Billion in 2035