Mental Health
Mental Health in Adolescents: How to Support Teenagers Facing Challenges
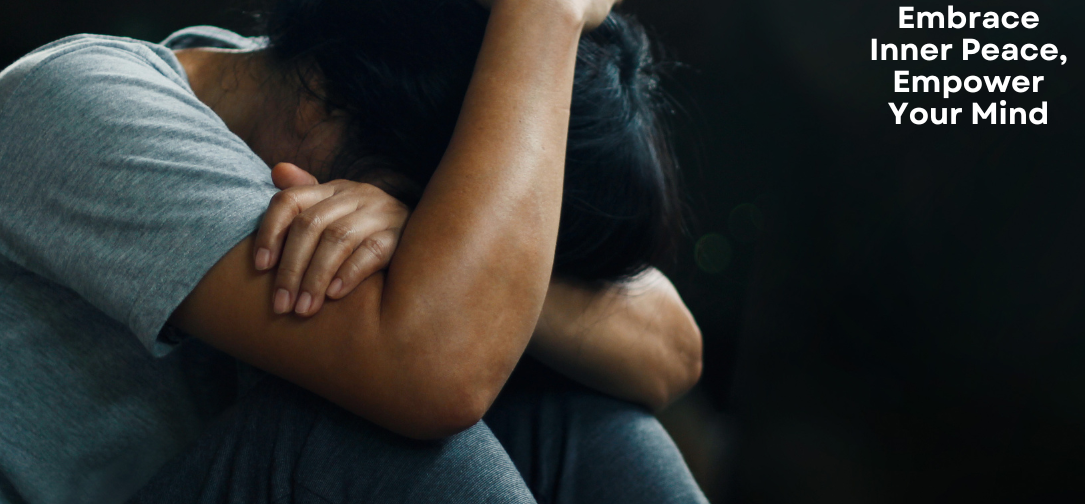

Adolescence is a critical period of development characterized by rapid physical, emotional, and social changes. It is a time when young people try to understand themselves and find their place in the world. Along with these changes, they often face numerous challenges that can significantly impact their mental health. Mental health issues among adolescents are on the rise globally, making it more crucial than ever to understand how to support teenagers facing these challenges effectively. This article delves deep into the complexities of adolescent mental health, the factors contributing to mental health issues, signs and symptoms, and practical strategies for providing support.
Understanding Adolescent Mental Health
Mental health is an integral part of overall health and well-being, encompassing emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It affects how individuals think, feel, and behave. For adolescents, mental health is a particularly sensitive area. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that one in seven adolescents aged 10–19 experiences mental health conditions. Half of all mental health conditions start by age 14, but most cases go undetected and untreated.
Adolescence is a period of life marked by profound changes. Puberty brings about significant hormonal fluctuations, leading to physical, cognitive, and emotional transformations. These changes can sometimes be overwhelming, leading to feelings of confusion, insecurity, and vulnerability. Adolescents are also faced with the challenge of establishing their identity, seeking independence from their parents, and finding a sense of belonging among peers. All these factors can have a profound impact on their mental health.
Factors Contributing to Adolescent Mental Health Issues
Understanding the factors that contribute to mental health issues in adolescents is essential for providing appropriate support. These factors can be broadly categorized into biological, psychological, social, and environmental influences:
1) Biological Factors: Genetics plays a crucial role in mental health. Adolescents with a family history of mental health disorders are more susceptible to experiencing similar issues. Neurobiological factors, such as hormonal imbalances and changes in brain structure and function during adolescence, can also contribute to mental health problems like depression, anxiety, and mood disorders.
2) Psychological Factors: Adolescents face numerous psychological stressors, including academic pressure, body image concerns, and the struggle for independence. Cognitive development during adolescence is characterized by increased abstract thinking, introspection, and self-consciousness. These cognitive changes can lead to increased susceptibility to negative thinking patterns, self-doubt, and anxiety.
3) Social Factors: Peer relationships are a significant source of support and stress for adolescents. Bullying, peer pressure, and social exclusion can have detrimental effects on mental health. Social media, while providing a platform for connection, can also contribute to issues like cyberbullying, unrealistic social comparisons, and feelings of inadequacy. Adolescents are highly sensitive to social acceptance and rejection, making them vulnerable to the impacts of social dynamics.
4) Environmental Factors: The home environment, family dynamics, and socio-economic status can significantly affect an adolescent’s mental health. Exposure to adverse childhood experiences (ACEs), such as abuse, neglect, parental separation, or substance abuse in the family, increases the risk of developing mental health disorders. Additionally, community factors like violence, lack of access to mental health services, and societal stigma around mental health issues can further exacerbate the problem.
Common Mental Health Disorders in Adolescents
Several mental health disorders commonly affect adolescents. Understanding these disorders and their symptoms is crucial for early identification and intervention:
1) Depression: Depression is one of the most prevalent mental health disorders among adolescents. It is characterized by persistent sadness, loss of interest in activities, changes in appetite and sleep patterns, fatigue, and feelings of hopelessness. Depression can severely affect an adolescent’s academic performance, social interactions, and overall quality of life.
2) Anxiety Disorders: Anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), social anxiety disorder, and panic disorder, are common among adolescents. Symptoms may include excessive worry, restlessness, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat and sweating. Anxiety can significantly impair daily functioning and social relationships.
3) Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): ADHD is characterized by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Adolescents with ADHD may struggle with academic performance, organizational skills, and maintaining focus. This disorder can lead to frustration, low self-esteem, and difficulties in peer relationships.
4) Eating Disorders: Eating disorders such as anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge-eating disorder often develop during adolescence. These disorders involve unhealthy eating behaviors, distorted body image, and an intense fear of gaining weight. Eating disorders can have severe physical and psychological consequences if left untreated.
5) Substance Use Disorders: Adolescents are at an increased risk of experimenting with substances such as alcohol, tobacco, and drugs. Substance use can be a coping mechanism for underlying mental health issues, but it often exacerbates the problem. Substance use disorders can lead to addiction, impaired judgment, and risky behaviors.
6) Self-Harm and Suicidal Behavior: Self-harm, such as cutting or burning oneself, is often a way for adolescents to cope with emotional pain. Suicidal ideation, planning, and attempts are alarmingly common among adolescents struggling with mental health issues. Suicide is the fourth leading cause of death among 15-19-year-olds globally.
Signs and Symptoms of Mental Health Issues in Adolescents
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of mental health issues in adolescents is crucial for early intervention and support. While each adolescent is unique, some common warning signs may indicate mental health struggles:
- Emotional Changes: Persistent sadness, irritability, mood swings, frequent crying, or emotional numbness.
- Behavioral Changes: Withdrawal from friends and family, loss of interest in activities, changes in eating and sleeping patterns, or sudden outbursts of anger.
- Academic Performance: Decline in academic performance, difficulty concentrating, or lack of motivation to attend school.
- Physical Symptoms: Unexplained headaches, stomachaches, or frequent visits to the school nurse.
- Risky Behaviors: Engaging in risky behaviors such as substance use, reckless driving, or unsafe sexual practices.
- Self-Harm: Visible cuts, burns, or bruises, or wearing long sleeves to hide injuries, even in hot weather.
- Talk of Death or Suicide: Statements like “I wish I were dead” or “Everyone would be better off without me” should never be ignored.
How to Support Teenagers Facing Mental Health Challenges
Supporting adolescents with mental health challenges requires a multifaceted approach that involves parents, caregivers, educators, healthcare providers, and the community. Here are some key strategies to provide effective support:
1) Create a Safe and Supportive Environment
- Open Communication: Encourage open and honest communication with adolescents. Let them know that it is okay to talk about their feelings and experiences without fear of judgment or punishment. Active listening is crucial – give them your full attention, validate their feelings, and avoid interrupting or dismissing their concerns.
-
Foster a Sense of Belonging: Adolescents need to feel a sense of belonging and acceptance. Encourage positive relationships with family, friends, and peers. Creating an inclusive and supportive environment at home and in school can help adolescents feel valued and understood.
- Educate About Mental Health: Educate adolescents about mental health, including the signs, symptoms, and importance of seeking help. Knowledge reduces stigma and empowers them to recognize when they or their peers might need support.
2) Promote Healthy Coping Strategies
- Encourage Physical Activity: Regular physical activity has been shown to have significant mental health benefits. Encourage adolescents to engage in sports, dance, or other physical activities they enjoy. Exercise helps reduce stress, anxiety, and depression while boosting self-esteem.
- Teach Stress-Management Techniques: Adolescents need to learn healthy ways to cope with stress and emotions. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and journaling can be effective in managing anxiety and improving emotional regulation.
- Limit Screen Time and Social Media Use: Excessive screen time and social media use have been linked to increased anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem in adolescents. Encourage a healthy balance of online and offline activities and monitor for signs of cyberbullying or harmful online behaviors.
3) Encourage Professional Help
Recognize the Need for Professional Support: If an adolescent is showing signs of severe mental health issues, it is essential to seek professional help. Psychologists, psychiatrists, and counselors are trained to provide the necessary support and interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), talk therapy, or medication.
Provide Access to Mental Health Resources: Ensure that adolescents have access to mental health resources, such as school counselors, hotlines, and mental health clinics. Providing information about these resources can empower them to seek help when needed.
Normalize Therapy and Counseling: Encourage a positive attitude toward therapy and counseling. Normalize seeking help as a proactive and responsible choice for managing mental health. Reducing the stigma around therapy can make adolescents feel more comfortable reaching out.
4) Build Resilience and Emotional Intelligence
Foster Emotional Intelligence: Teach adolescents to identify and understand their emotions and the emotions of others. Building emotional intelligence helps them navigate social relationships, manage conflicts, and make responsible decisions.
Encourage Problem-Solving Skills: Encourage adolescents to develop problem-solving skills and resilience. Teach them to approach challenges as opportunities for growth rather than as insurmountable obstacles.
Promote a Growth Mindset: Encourage a growth mindset, where adolescents believe that abilities and intelligence can be developed through effort and learning. This mindset fosters resilience and persistence in the face of difficulties.
5) Involve the Community and Schools
- School-Based Mental Health Programs: Schools play a crucial role in adolescent mental health. Implementing school-based mental health programs can provide early intervention and support. These programs can include peer support groups, mental health education, and access to school counselors.
- Community Support Networks: Community organizations, such as youth centers, sports clubs, and religious groups, can provide additional support networks for adolescents. Engaging adolescents in community activities can help them build social connections and reduce feelings of isolation.
- Advocate for Mental Health Awareness: Advocate for mental health awareness and policies that promote access to mental health services and reduce stigma. Schools, communities, and governments need to work together to create an environment that supports adolescent mental health.
Conclusion
Adolescent mental health is a complex and multifaceted issue that requires a comprehensive approach to support teenagers facing challenges. Understanding the factors contributing to mental health issues, recognizing the signs and symptoms, and providing appropriate support are crucial steps in helping adolescents navigate this critical stage of life. By creating a safe and supportive environment, promoting healthy coping strategies, encouraging professional help, building resilience, and involving the community and schools, we can make a significant difference in the mental well-being of adolescents. As a society, we have a collective responsibility to ensure that our young people receive the care, support, and understanding they need to thrive and grow into healthy, well-adjusted adults.
-

 Food12 hours ago
Food12 hours agoHow to Lose Weight Fast: The Best Drink Recipes for Rapid Results
-

 Education12 hours ago
Education12 hours agoUnlocking the ASUS Student Discount on Reddit: A Comprehensive Guide
-

 News5 hours ago
News5 hours agoUnfiltered: Behind the Headlines with Page Six
-

 Banking9 hours ago
Banking9 hours agoUnlock Your Financial Potential with SoFi High-Yield Savings