Mental Health
Mental Health First Aid: How to Help Someone in Crisis

Mental health crises are increasingly common in today’s world, impacting individuals, families, and communities. These crises can manifest in various forms, such as severe anxiety, depression, psychosis, or suicidal ideation. Understanding how to respond effectively to someone in a mental health crisis is crucial, as timely intervention can make a significant difference in their recovery journey. Mental Health First Aid (MHFA) is an invaluable tool that equips individuals with the skills to offer initial support and guide someone experiencing a mental health problem or crisis. This article delves into the principles, techniques, and importance of Mental Health First Aid, providing a comprehensive guide on how to help someone in crisis.
What is Mental Health First Aid?
Mental Health First Aid is a training program that teaches people how to identify, understand, and respond to signs of mental health issues. Similar to physical first aid, MHFA aims to provide initial support until professional help is available or until the crisis resolves. Developed by Betty Kitchener and Anthony Jorm in Australia in 2000, MHFA has since been adopted globally, with tailored courses available for various groups, including youth, veterans, and workplace settings.
Core Principles of MHFA
The foundation of Mental Health First Aid is built on several core principles:
1) Non-Judgmental Support: Approach the individual without judgment or stigma. Listen and communicate in a way that respects their feelings and perspectives.
2) Confidentiality: Protect the individual’s privacy and only share information with those directly involved in their care or safety.
3) Empowerment: Encourage the person to take control of their situation by making decisions that promote their well-being.
4) Cultural Sensitivity: Be aware of and respect cultural differences in attitudes towards mental health and help-seeking behaviors.
5) Safety First: Prioritize the safety of both the person in crisis and yourself. If there is an immediate risk of harm, contact emergency services.
The ALGEE Action Plan
The MHFA action plan is known by the acronym ALGEE, which stands for:
1) Assess for Risk of Suicide or Harm: The first step involves determining if the person is at risk of self-harm or harm to others. This may require direct questioning about suicidal thoughts or plans.
2) Listen Non-Judgmentally: Offer an empathetic ear without interrupting, criticizing, or judging. Active listening can help the person feel understood and validated.
3) Give Reassurance and Information: Provide reassurance that mental health challenges are treatable and that help is available. Offer accurate information about mental health resources.
4) Encourage Appropriate Professional Help: Suggest seeking help from mental health professionals, such as psychiatrists, psychologists, or counselors, who can offer tailored treatment.
5) Encourage Self-Help and Other Support Strategies: Promote healthy coping mechanisms like exercise, relaxation techniques, and social support networks.
Understanding Different Types of Mental Health Crises
A mental health crisis can present in various forms, each requiring a unique response approach. Below are some common types of crises and how to respond effectively.
Suicidal Ideation
Suicidal thoughts are a severe crisis that requires immediate attention. If someone expresses thoughts of suicide, it’s crucial to:
1) Ask Directly About Suicide: Contrary to common belief, asking about suicide does not plant the idea in someone’s mind. Be direct: “Are you thinking about suicide?”
2) Remove Access to Means: If possible and safe, remove any items that the person could use to harm themselves, such as firearms, medications, or sharp objects.
3) Stay With Them: Do not leave the person alone until professional help is available. Your presence can provide significant emotional support and reduce the risk of immediate harm.
4) Seek Professional Help Immediately: Call emergency services or take the person to the nearest emergency room. If they are reluctant, explain the importance of getting help.
Panic Attacks
Panic attacks can be overwhelming and frightening, but they are not life-threatening. To help someone experiencing a panic attack:
1) Stay Calm: Your calm presence can help soothe the person. Speak in a gentle and reassuring voice.
2) Encourage Slow Breathing: Guide the person to take deep, slow breaths. Breathing exercises can help reduce the symptoms of a panic attack.
3) Use Grounding Techniques: Encourage the person to focus on their surroundings by identifying objects they can see, hear, touch, or smell. This can help bring their attention away from the panic and back to the present moment.
4) Avoid Minimizing Their Experience: Statements like “just calm down” or “it’s all in your head” are not helpful. Instead, validate their feelings by saying, “I know this feels overwhelming, but it will pass.”
Psychotic Episodes
Psychosis involves a disconnection from reality and may include hallucinations or delusions. To support someone experiencing psychosis:
1) Stay Calm and Avoid Confrontation: Do not argue with the person about their hallucinations or delusions. Instead, acknowledge their feelings and express empathy.
2) Provide a Safe Environment: Reduce noise, bright lights, or other stimuli that may exacerbate their symptoms. Create a calm and safe space.
3) Seek Professional Help: Psychosis often requires medical intervention. Encourage the person to see a mental health professional as soon as possible.
4) Do Not Make Sudden Movements: Approach the person slowly and avoid sudden movements, which may be perceived as threatening.
Severe Anxiety and Depression
Severe anxiety and depression can significantly impair a person’s ability to function. Here’s how to offer support:
1) Encourage Open Communication: Invite the person to talk about their feelings if they feel comfortable. Listen actively without offering unsolicited advice.
2) Offer Practical Support: Help with daily tasks that may seem overwhelming to the person, such as running errands or preparing meals.
3) Promote Professional Help: Suggest consulting with a healthcare provider who can provide a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
4) Be Patient: Recovery from anxiety and depression can be a slow process. Offer ongoing support without pressuring the person to “snap out of it.”
The Importance of Mental Health First Aid in the Community
Mental Health First Aid is not just for healthcare professionals; it’s for everyone. The training empowers individuals to make a positive impact in their communities by:
1) Reducing Stigma: MHFA promotes understanding and acceptance of mental health issues, challenging the stigma that often prevents people from seeking help.
2) Increasing Awareness: Participants gain a deeper understanding of various mental health conditions, how they manifest, and how they can be managed.
3) Building Support Networks: MHFA fosters a supportive community where individuals feel safe discussing their mental health and seeking assistance.
4) Encouraging Early Intervention: Recognizing the signs of mental health issues early can lead to timely intervention, reducing the severity and duration of a crisis.
Mental Health First Aid in the Workplace
Workplaces are increasingly adopting MHFA training to support employee well-being. Stress, burnout, and mental health issues are common in high-pressure environments. By integrating MHFA into workplace policies, organizations can:
1) Create a Supportive Environment: Employees trained in MHFA can offer peer support, creating a culture of care and compassion.
2) Improve Productivity: Addressing mental health issues proactively can reduce absenteeism and increase productivity
3) Enhance Employee Retention: A supportive workplace fosters loyalty and reduces turnover, as employees feel valued and understood.
4) Mitigate Risk: Early intervention can prevent crises from escalating, reducing the risk of workplace accidents or conflicts.
Barriers to Implementing Mental Health First Aid
Despite its benefits, implementing MHFA can face several challenges:
1) Stigma and Misconceptions: Misunderstandings about mental health and reluctance to discuss these issues openly can hinder the effectiveness of MHFA programs.
2) Resource Limitations: Access to training and resources can be limited, particularly in low-income or rural areas.
3) Cultural Barriers: Cultural beliefs and attitudes towards mental health can affect how people perceive and engage with MHFA.
4) Lack of Follow-up Support: MHFA provides initial assistance, but ongoing support and professional intervention are crucial for recovery. Without proper referral pathways, the effectiveness of MHFA may be limited.
Strategies to Enhance the Effectiveness of MHFA
To maximize the impact of MHFA, the following strategies can be employed:
1) Regular Training and Refreshers: Ongoing education ensures that participants stay up-to-date with the latest knowledge and skills.
2) Creating Support Networks: Establishing networks of MHFA-trained individuals within communities or organizations can provide continuous support and reduce isolation.
3) Integration with Professional Services: Building strong connections with local mental health services ensures that individuals can be referred promptly for further help.
4) Promoting Awareness Campaigns: Public campaigns can reduce stigma and encourage more people to seek MHFA training.
5) Tailoring Training to Specific Needs: Customizing MHFA courses for particular groups, such as youth, indigenous communities, or veterans, increases relevance and effectiveness.
The Future of Mental Health First Aid
As mental health issues continue to rise globally, the role of Mental Health First Aid is likely to expand. Future directions may include:
1) Digital and Online Training: Expanding online training options can make MHFA more accessible to people in remote or underserved areas.
2) Integration with Schools and Universities: Early intervention in educational settings can help address mental health issues before they escalate.
3) Workplace Policies and Legislation: Governments and organizations may increasingly mandate MHFA training as part of occupational health and safety policies.
4) Global Expansion: Continued efforts to introduce MHFA in developing countries will help address the global mental health crisis.
Conclusion
Mental Health First Aid is a vital tool in addressing the growing mental health crisis. By equipping individuals with the skills to recognize and respond to mental health issues, MHFA can save lives, reduce stigma, and promote recovery. Whether in the workplace, schools, or community settings, MHFA empowers people to provide crucial support during times of crisis, ensuring that those in need receive the help they deserve. In a world where mental health challenges affect millions, understanding how to help someone in crisis is more important than ever.
-
 Press Release4 days ago
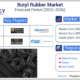
Press Release4 days agoClinical Trials Market Set for Robust Growth, Driven by Drug Development Surge and Digital Innovation
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoFill-Finish Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Market Expected to Flourish Amid Biopharmaceutical Boom and Global Outsourcing Trend by 2035
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoHow Managed IT Solutions Help Small Teams Compete at Enterprise Scale
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoGreen Bio Chemicals Market Poised for Sustainable Growth amidst Global Shift to Eco-Friendly Alternatives by 2035
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoIndustrial Boiler Market Expected to Surpass USD 24.4 Billion by 2035 Amid Growing Demand for Energy Efficiency and Industrialization
-
 Press Release5 days ago
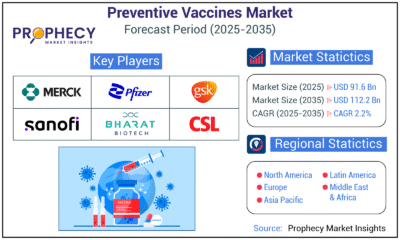
Press Release5 days agoPreventive Vaccines Market to Witness Strong Growth by 2035
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoPet Food Nutraceutical Market Set for Robust Expansion Amid Rising Demand for Pet Wellness by 2035
-

 Press Release4 days ago
Press Release4 days agoWaterproof Structural Adhesives Market: A Comprehensive Study Towards USD 10.3 Billion in 2035