Health & Fitness
Men’s Health Issues: The Importance of Regular Checkups and Screenings
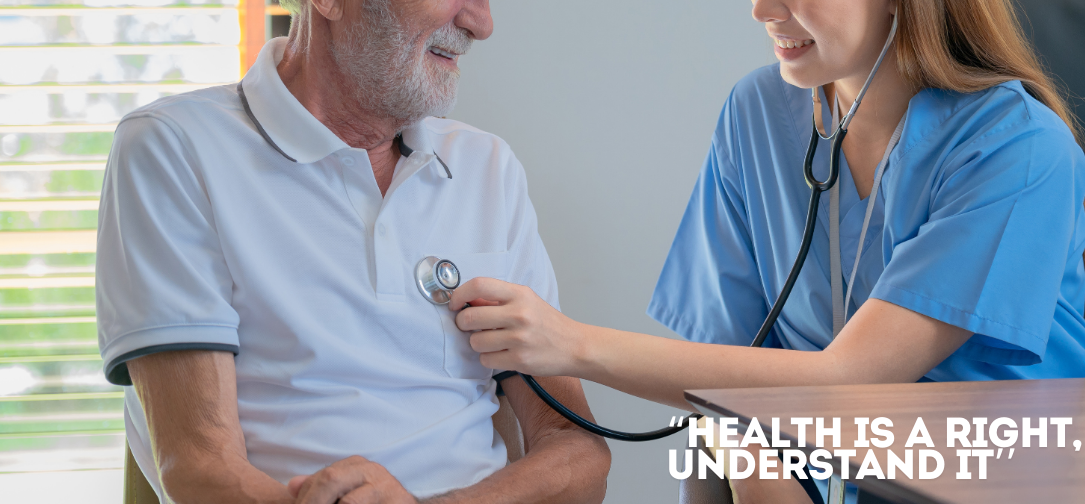

Men often neglect their well-being, delaying visits to the doctor until a problem becomes too serious to ignore. This tendency to avoid medical appointments and screenings can be detrimental, leading to the late diagnosis of conditions that could have been managed or even prevented with early intervention. Men’s health encompasses a broad spectrum of issues, from cardiovascular diseases and mental health to prostate cancer and sexual health. Regular checkups and screenings are not merely routine procedures; they are critical for early detection, prevention, and management of diseases. In this comprehensive discussion, we delve into the importance of regular health checkups for men, the barriers to seeking medical care, and the various health screenings that can save lives.
The State of Men’s Health
Men’s health is an area of concern globally, with several studies indicating that men are more likely than women to delay seeking medical help, underutilize preventive care services, and suffer from various health conditions. Statistically, men are at a higher risk of developing severe health issues such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), men die on average five years earlier than women, and this gap can be attributed largely to preventable health problems. Many men continue to face avoidable health challenges due to a combination of behavioral, social, and cultural factors.
Behavioral Factors
Men are often conditioned from a young age to exhibit strength, endurance, and self-reliance. This mindset can foster a culture where seeking help is viewed as a sign of weakness, particularly when it comes to physical and mental health. This reluctance to seek help manifests in the form of neglecting regular health checkups, avoiding discussions about health concerns, and being less likely to report symptoms of illness. This can lead to delays in diagnosing and treating diseases, some of which can progress rapidly without early intervention.
Social and Cultural Influences
Societal expectations and cultural norms play a significant role in shaping men’s health behaviors. The traditional male gender role emphasizes toughness, emotional stoicism, and the suppression of vulnerability, making it difficult for many men to engage in proactive health-seeking behaviors. Furthermore, men are less likely to participate in community health programs and are often less informed about the importance of preventive care and early screenings.
The Economic Aspect
Economic factors also contribute to the disparity in men’s health. In many households, men are perceived as primary breadwinners, and taking time off work for medical appointments can seem impractical or unnecessary. Moreover, financial constraints and a lack of health insurance coverage are significant barriers that prevent many men from accessing regular healthcare services.
The Importance of Regular Checkups
Regular health checkups play a crucial role in maintaining overall well-being and preventing the onset of life-threatening diseases. For men, these checkups serve several essential functions:
1) Early Detection of Diseases: Regular visits to a healthcare provider enable early detection of diseases such as hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol, which often do not present noticeable symptoms until they reach advanced stages. Early diagnosis allows for timely intervention and management, reducing the risk of complications and improving the prognosis.
2) Monitoring Existing Conditions: For men who have been diagnosed with chronic conditions like diabetes, cardiovascular disease, or respiratory problems, regular checkups help in monitoring the status and effectiveness of the treatment. Adjustments to medications, lifestyle, and diet can be made based on the results of routine assessments.
3) Preventive Care and Vaccinations: Preventive healthcare includes vaccinations, screenings, and counseling on lifestyle changes that can prevent diseases. Men who regularly engage in preventive care are more likely to avoid serious illnesses and maintain a higher quality of life as they age.
4) Mental Health Awareness: Regular checkups also provide an opportunity for healthcare professionals to assess mental health. Depression, anxiety, and stress-related disorders are common but often underreported in men. Open discussions with a healthcare provider can facilitate early diagnosis and management of mental health issues.
5) Establishing a Doctor-Patient Relationship: Building a strong, trusting relationship with a healthcare provider encourages men to be more forthcoming about their symptoms and concerns, resulting in better healthcare outcomes.
Critical Screenings and Checkups for Men
For men, health screenings and checkups are essential at every stage of life. The frequency and type of screenings required can vary based on age, family history, lifestyle, and risk factors. Here are some of the most crucial screenings men should consider:
1) Blood Pressure Screening
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is often called the “silent killer” because it rarely presents symptoms until it causes significant damage. Uncontrolled hypertension can lead to heart disease, stroke, kidney damage, and other severe conditions. Men should have their blood pressure checked at least once every two years, starting in their 20s. If a man has a family history of hypertension or other risk factors like obesity, diabetes, or smoking, more frequent monitoring is necessary.
2) Cholesterol Screening
High cholesterol is another silent condition that increases the risk of heart disease and stroke. Men should have their cholesterol levels checked every 4-6 years, starting at age 20. For those with additional risk factors, such as a family history of heart disease, diabetes, or obesity, cholesterol screenings may need to occur more frequently.
3) Diabetes Screening
Type 2 diabetes is a growing health concern worldwide, particularly in men who are overweight, lead sedentary lifestyles, or have a family history of diabetes. Men aged 45 and older should have their blood sugar levels checked every three years. For men with risk factors such as obesity, high blood pressure, or a sedentary lifestyle, earlier and more frequent screenings may be advisable.
4) Prostate Cancer Screening
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting men. The prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test and digital rectal exam (DRE) are the primary screening tools used to detect prostate cancer in its early stages. Men should discuss the risks and benefits of prostate cancer screening with their healthcare provider, particularly if they are aged 50 or older. Those with a family history of prostate cancer or of African American descent may need to start screening earlier.
5) Colorectal Cancer Screening
Colorectal cancer is the third most common cancer in men. Screening is essential because it can detect precancerous polyps that can be removed before they become cancer. Men aged 50 and older should undergo regular screenings, such as a colonoscopy, every 10 years or more frequently, depending on their risk factors. Men with a family history of colorectal cancer or inflammatory bowel disease may need to start screenings earlier.
6) Testicular Cancer Screening
Testicular cancer is relatively rare but predominantly affects younger men, particularly those between the ages of 15 and 35. Self-examination and awareness of changes in the testicles can aid in early detection. Men should discuss testicular cancer screening during routine checkups, especially if they have risk factors such as a family history or an undescended testicle.
7) Bone Density Test
Osteoporosis is often considered a women’s disease, but men are also at risk, especially as they age. Men over 70 or those over 50 with risk factors such as low body weight, a history of fractures, or steroid use should have bone density tests to assess their risk of osteoporosis.
8) Mental Health Screening
Mental health issues, including depression, anxiety, and stress, can significantly impact men’s lives. Unfortunately, these conditions are often underdiagnosed in men due to stigma and the reluctance to seek help. Regular checkups should include mental health screenings to ensure timely diagnosis and intervention.
9) Skin Cancer Screening
Men are more likely than women to develop and die from melanoma, the most deadly form of skin cancer. Regular skin examinations by a dermatologist, especially for those with fair skin, a history of sunburns, or a family history of skin cancer, are essential.
10) Sexual and Reproductive Health
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can have serious health consequences if left untreated. Men should have open discussions with their healthcare providers about their sexual health and undergo regular screenings for STIs, particularly if they have multiple partners or are at higher risk.
Overcoming Barriers to Men’s Health
To improve men’s health outcomes, it is crucial to address the barriers that prevent men from seeking regular checkups and screenings. Here are some strategies to encourage men to take charge of their health:
Education and Awareness Campaigns: Public health campaigns that focus on raising awareness about the importance of regular checkups and screenings can help change the narrative around men’s health. Providing information on the benefits of early detection and the availability of services can empower men to make informed decisions about their health.
Workplace Wellness Programs: Given that men often cite lack of time as a reason for not seeking medical care, workplace wellness programs can offer convenient health checkups and screenings options. On-site health clinics, wellness incentives, and flexible scheduling can encourage men to prioritize their health.
Reducing Stigma Around Seeking Help: Promoting a culture where seeking help is seen as a strength rather than a weakness is vital. This involves changing societal norms and encouraging men to talk openly about their health concerns without fear of judgment.
Engaging Healthcare Providers: Healthcare providers play a crucial role in engaging men in conversations about their health. Providers should adopt a non-judgmental and supportive approach, encouraging men to be proactive about their health.
Family and Social Support: Family members, particularly partners and spouses, can play a significant role in encouraging men to attend regular checkups and screenings. Open communication within families about the importance of health can lead to better health outcomes.
Conclusion
Men’s health issues are multifaceted and require a comprehensive approach to address them effectively. Regular checkups and screenings are fundamental in detecting health problems early, managing chronic conditions, and preventing diseases. By understanding the barriers that prevent men from seeking regular medical care and implementing strategies to overcome these barriers, we can significantly improve men’s health outcomes. It is essential for men to break free from societal norms that discourage them from prioritizing their health and to recognize that taking care of one’s health is not a sign of weakness but a hallmark of responsibility and strength.
Regular checkups and screenings are investments in one’s future well-being. They not only extend life expectancy but also improve the quality of life. As the conversation around men’s health continues to evolve, it is crucial to foster a culture where health-seeking behavior is normalized and encouraged, ultimately leading to healthier and more fulfilling lives for men worldwide.
-
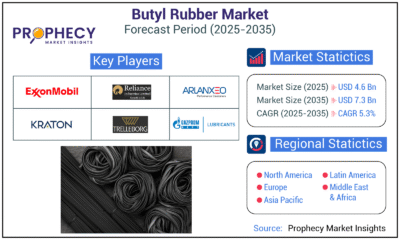
 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoClinical Trials Market Set for Robust Growth, Driven by Drug Development Surge and Digital Innovation
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoHow Managed IT Solutions Help Small Teams Compete at Enterprise Scale
-

 Press Release6 days ago
Press Release6 days agoGreen Bio Chemicals Market Poised for Sustainable Growth amidst Global Shift to Eco-Friendly Alternatives by 2035
-

 Press Release6 days ago
Press Release6 days agoFill-Finish Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Market Expected to Flourish Amid Biopharmaceutical Boom and Global Outsourcing Trend by 2035
-

 Press Release6 days ago
Press Release6 days agoIndustrial Boiler Market Expected to Surpass USD 24.4 Billion by 2035 Amid Growing Demand for Energy Efficiency and Industrialization
-
 Press Release6 days ago
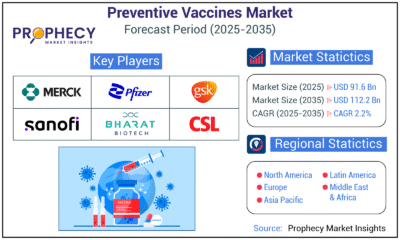
Press Release6 days agoPreventive Vaccines Market to Witness Strong Growth by 2035
-

 Press Release6 days ago
Press Release6 days agoPet Food Nutraceutical Market Set for Robust Expansion Amid Rising Demand for Pet Wellness by 2035
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoPediatric Vaccines Market: Safeguarding Futures, Driving Growth