Medical
Heart Disease: The Silent Killer and How to Prevent It
Heart disease, often termed the “silent killer,” remains the leading cause of death globally, responsible for an estimated 17.9 million lives annually. This condition encompasses a range of disorders that affect the heart, including coronary artery disease, arrhythmias, heart valve issues, and heart failure. Despite advancements in medical science, heart disease continues to pose a significant threat to public health, primarily because it can progress silently, without noticeable symptoms, until a life-threatening event, such as a heart attack or stroke, occurs.
The Silent Progression of Heart Disease
One of the most insidious aspects of heart disease is its often asymptomatic nature in its early stages. Conditions like hypertension (high blood pressure) and atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) can develop over years, quietly causing damage to the cardiovascular system. Hypertension, in particular, is a critical risk factor, often referred to as the “silent killer” because it rarely presents symptoms until severe damage has occurred. High blood pressure can lead to a variety of cardiovascular complications, including heart attacks, strokes, and heart failure.
A study published in The Healthy highlights the importance of maintaining blood pressure within a specific range to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events. The research suggests that systolic blood pressure (the upper number in a blood pressure reading) should ideally be maintained between 120 and 139 mmHg to minimize mortality rates related to heart disease. This range aligns with guidelines in several countries, although there are slight variations based on regional health recommendations.
Heart Disease Statistics and Global Impact
The global burden of heart disease is staggering. In the United States alone, heart disease is responsible for one in every four deaths. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that approximately 697,000 people died from heart disease in the U.S. in 2020, making it the leading cause of death in the country. Worldwide, the situation is even more dire, with millions of individuals affected by various forms of cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Despite the availability of preventive measures and treatment options, heart disease remains prevalent due to a combination of factors, including lifestyle choices, genetic predisposition, and socioeconomic conditions. For instance, communities with limited access to healthcare, healthy foods, and opportunities for physical activity are disproportionately affected by heart disease. This highlights the importance of public health initiatives to reduce health disparities and promote heart-healthy behaviors.
Prevention Strategies: A Multifaceted Approach
Preventing heart disease requires a comprehensive approach that involves lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, and public health policies. Key strategies for prevention include
- Healthy Diet: A heart-healthy diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, such as nuts, seeds, and fish. Reducing the intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and sodium is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health. Excessive sodium intake, in particular, has been linked to high blood pressure, a major risk factor for heart disease. The American Heart Association recommends limiting daily sodium intake to 1,500 mg for most adults.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, lowers blood pressure, and improves overall cardiovascular health. The CDC recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity each week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days a week.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease, contributing to the buildup of plaque in the arteries (atherosclerosis) and increasing the likelihood of heart attacks and strokes. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease, even in long-term smokers. Programs that provide counseling, medication, and support can greatly increase the chances of successfully quitting.
- Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Management: Regular monitoring and management of blood pressure and cholesterol levels are essential for preventing heart disease. High blood pressure and high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol are major contributors to the development of heart disease. Medications, along with lifestyle changes, can effectively control these risk factors and reduce the likelihood of cardiovascular events.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact heart health by increasing blood pressure and contributing to unhealthy behaviors, such as poor diet and physical inactivity. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and regular physical activity can help manage stress and improve overall well-being.
- Screening and Early Detection: Regular health screenings, including blood pressure checks, cholesterol tests, and assessments of other risk factors, are crucial for early detection and management of heart disease. For those at higher risk, more advanced screenings, such as coronary artery calcium scoring, may be recommended to assess the presence of plaque in the arteries.
Public Health Initiatives and Technological Advancements
Public health initiatives play a vital role in combating heart disease by promoting healthy behaviors, improving access to care, and addressing social determinants of health. The CDC’s Million Hearts initiative, launched in 2012, is one such effort aimed at preventing one million heart attacks and strokes within five years. The initiative focuses on improving the “ABCS” of heart health—Aspirin use when appropriate, Blood pressure control, Cholesterol management, and Smoking cessation.
Additionally, technological advancements are enhancing the ability to prevent and manage heart disease. The use of artificial intelligence (AI) and big data analytics is enabling healthcare providers to identify at-risk populations, tailor interventions, and monitor patient outcomes more effectively. Wearable devices and mobile health applications are also empowering individuals to take control of their heart health by tracking their physical activity, heart rate, and other vital signs in real-time.
The Importance of Ongoing Research and Funding
Despite the progress made in understanding and preventing heart disease, significant challenges remain. Continued research is essential to uncover new insights into the causes and treatment of heart disease. Moreover, adequate funding is critical to support public health initiatives, research efforts, and the development of innovative therapies.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, heart disease prevention efforts faced setbacks as healthcare resources were diverted to address the immediate crisis. However, as the world emerges from the pandemic, there is an urgent need to refocus on heart disease prevention and ensure that resources are allocated to combat this ongoing public health threat.
Conclusion
Heart disease remains a formidable challenge, but it is also one of the most preventable chronic conditions. By adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, managing risk factors, and supporting public health initiatives, individuals and communities can significantly reduce the burden of heart disease. As a society, it is crucial to prioritize heart health and invest in the research, education, and resources needed to combat this silent killer effectively.
For more detailed information on preventing heart disease and managing risk factors, you can visit reputable sources such as the American Heart Association, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and The Healthy by Reader’s Digest.
-
 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoClinical Trials Market Set for Robust Growth, Driven by Drug Development Surge and Digital Innovation
-

 Press Release6 days ago
Press Release6 days agoGreen Bio Chemicals Market Poised for Sustainable Growth amidst Global Shift to Eco-Friendly Alternatives by 2035
-

 Press Release6 days ago
Press Release6 days agoIndustrial Boiler Market Expected to Surpass USD 24.4 Billion by 2035 Amid Growing Demand for Energy Efficiency and Industrialization
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoHow Managed IT Solutions Help Small Teams Compete at Enterprise Scale
-

 Press Release6 days ago
Press Release6 days agoFill-Finish Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Market Expected to Flourish Amid Biopharmaceutical Boom and Global Outsourcing Trend by 2035
-
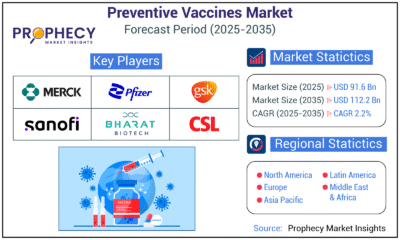
 Press Release6 days ago
Press Release6 days agoPreventive Vaccines Market to Witness Strong Growth by 2035
-

 Press Release6 days ago
Press Release6 days agoPet Food Nutraceutical Market Set for Robust Expansion Amid Rising Demand for Pet Wellness by 2035
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoWaterproof Structural Adhesives Market: A Comprehensive Study Towards USD 10.3 Billion in 2035