


Having equal access and opportunity in the healthcare system will help save lives. One of the biggest problems facing the healthcare industry is that there is...



Tick-borne illnesses, particularly Lyme disease, are emerging as a significant public health concern worldwide. These diseases, transmitted primarily by ticks, have surged in prevalence over the...
Emerging infectious diseases (EIDs) pose a significant threat to global health, economic stability, and social structures. These diseases, often caused by pathogens previously unknown or not...
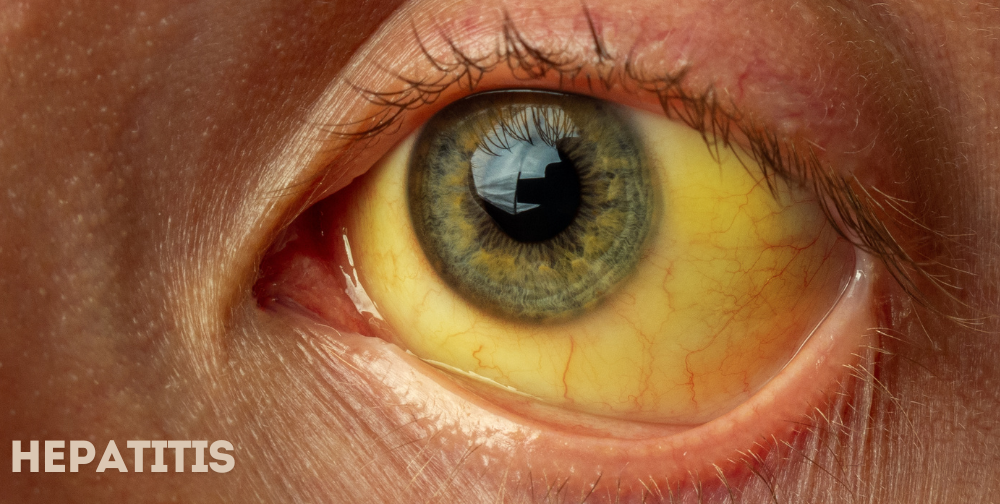
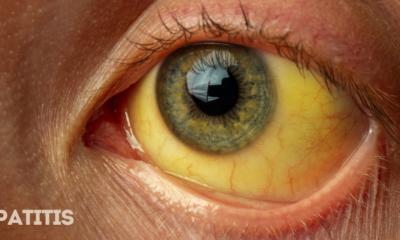
Hepatitis is a term that refers to inflammation of the liver, often caused by a viral infection. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), viral hepatitis...
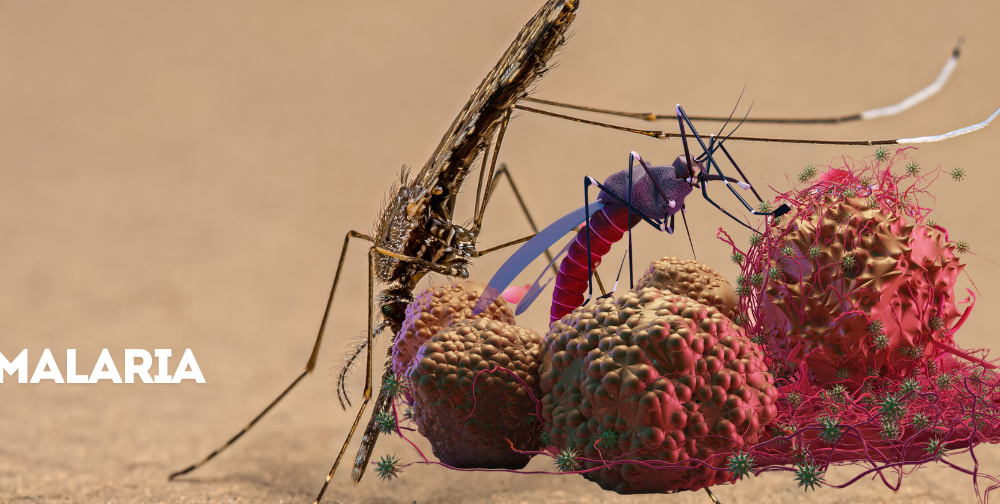


According to the World Health Organization (WHO), there were 249 million cases of malaria in 2022, with an estimated 608,000 deaths, most of which occurred in...



Food safety is a critical concern worldwide, especially at home, where improper handling and preparation of food can lead to foodborne illnesses. The Centers for Disease...



Waterborne diseases primarily spread through drinking or using contaminated water. Contamination can occur from a variety of sources, including human and animal waste, agricultural runoff, and...
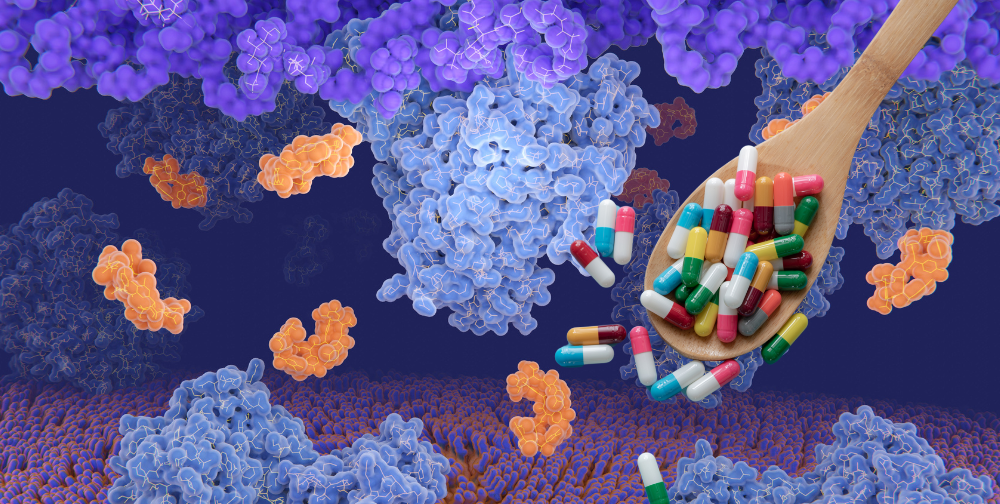
Antibiotic resistance is one of the most pressing health challenges of the 21st century, representing a global threat to public health, food security, and development. Once...



Air pollution is an invisible menace that affects millions of people worldwide. Its insidious effects go beyond the obvious smog-filled skies or the industrial chimneys belching...
Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the most significant global health challenges today, with over 10 million new cases and 1.6 million deaths annually, making it the...