Computers & IT
How to Master Pareto Chart in 6 Simple Steps
Learn how to create different types of Pareto chart with very simple and brief examples
Understanding the key issues and their causes can be complicated for you, so you spend your time-solving problems that have the least effect on the project. In such cases, the Pareto Chart can be useful in resolving issues. Pareto Map is one of the seven fundamental methods of quality control. The Pareto Diagram assists you in distinguishing between defects and their causes. If you know Pareto Chart, you can concentrate on the trigger that is causing the most problems. Pareto is a crucial tool in quality control, and project managers use it to identify the most critical cases. Pareto Charts are used to prioritize problems to identify the most important ones.
Pareto analysis, the 80/20 rule, is a commonly used and straightforward method for prioritizing problem-solving opportunities. Learn how to make a Pareto graph in Excel and how to view it step by step. It’s used to distinguish the most significant causes of an issue from the many minor ones. This theory states that 20% of the trigger will cause 80% of the problem’s effects.
80:20 Rule:
The Pareto Chart is used to rank the contributors who have the greatest effect on an issue or represent the most opportunities. The 80/20 rule claims that 20% of the causes account for 80% of the impact, considering the following scenario:
- 20% of the customers account for 80% of the revenue.
- Only 20% of customers contribute to sales.
- Few reasons account for 80% of all consumer complaints
- The few troublesome areas consume 80% of the repair and maintenance time.
Essentially, the 80/20 rule states that concentrating on the critical few produces great results than focusing on the insignificant many. The Pareto map is a method used to concentrate attention on goals while making decisions. It’s an effective communication tool because it represents data in a simple and easy-to-understand bar diagram. Pareto graph aids in the study and analysis of the frequency of occurrences of an event in a phase and the identification of the major contributors.
Benefits of Using a Pareto Chart:
There are several advantages of using a Pareto Map concerning economics. A Pareto Chart is a diagram that depicts the relationship between two variables.
- Breaks down a larger issue into smaller chunks.
- Identifies the most important factors and indicates where resources need to be focused.
- Allows for more effective utilization of scarce resources.
It will help if you focus on the improvement efforts by distinguishing the few key issues from the many likely problems, grouping data by priority or significance, and deciding the problems that should be bothered.
Questions that Can Be Answered Using the Pareto Chart:
- What are the most pressing issues confronting the team or company?
- What are 20% of sources responsible for 80% of the problems?
- Where do we focus our efforts to make the most progress?
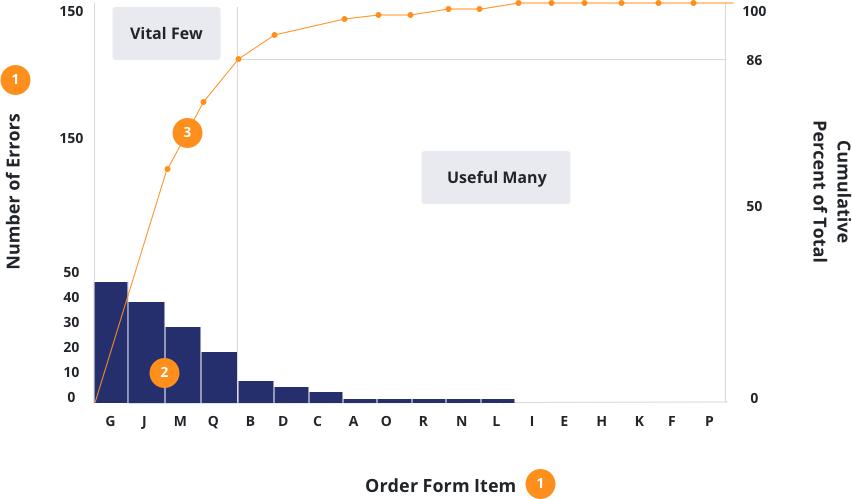
Illustration of The Pareto Chart Prototype:
Let’s have a look at the example of a Pareto map. In the first table, you will see the raw data. It has two columns, one for defect form and the other for defect count.
- To draw the Pareto map, you have first to arrange the raw data in a meaningful manner. The information is presented in descending order.
- Then, you add up the totals in the ‘Count of Defects’ tab. Then, divide each observation in the ‘Count of Defects’ column by the total of the ‘Percentage’ column.
- To measure the percentage contribution, divide the observation by total and multiply the result by 100, and so on.
- Measure the total percentage for each observation in the ‘Percentage’ column in the cumulative percent column. To begin the calculation, copy the observation figure and paste it into the ‘Cumulative percent’ column.
- Eventually, the observed percentage figure is applied to arrive at a total percentage. The calculation should be carried on until you reach the last column.
- The data is now said to be structured in a way that allows you to plot the Pareto chart.
Defect types account for nearly 80% of the issues. To improve the operation, the Six Sigma project team should concentrate on these defect forms.
Excel-based Pareto Map:
Pareto analysis is extremely useful in assisting management in determining the most relevant and impactful issues or defect areas and directing corrective action resources to the appropriate locations. Making a Pareto chart in MS Excel is easy, but you must first grasp the principle and master a few measures.
Step 1:
First, make a list of causes or defects, along with their frequency, in an excel table. Here, an example of customer complaint calls is taken into consideration. An audit of 300 calls on 12 parameters is specified, with the number of defects noted under ‘CSQ Parameters.’
Step 2:
Phase 2 allows you to sort the data in descending order. Many people tend to forget this move, resulting in a Pareto chart that does not resemble a Pareto Chart.
Step 3:
Here, you’ll need to add a column for each defect type’s proportion/percent contribution. Add a column for the cumulative proportion. The cumulative proportion will depict the impact of all parameters added together.
Step 4:
Compute the total proportion. The cumulative cell’s first cell has the same importance as the first cell of the proportion cell. Calculating the cumulative proportion is quite simple. The first row will have the same value as the ‘Proportion’ column, and the second row is used to apply the formula.
Step 5:
In this step, pick the first and second columns and the ‘cumulative’ column and then select ‘Recommended Charts’ from the ‘Insert’ menu. Choose the Pareto Chart option from the drop-down menu.
Conclusion:
Pareto analysis is extremely helpful in assisting management in determining the most relevant and impactful issues. However, when creating a Pareto map, you don’t account for the severity of various types of defects. To use Pareto analysis, you must first recognize the list and issues you’re dealing with, as well as their root causes. Then, allocate a score to each issue based on its importance. The scoring system depends on the types of problems you attempt to fix. Pareto Chart is based solely on the frequency in which an incident or defect occurs.
-

 Food18 hours ago
Food18 hours agoHow to Lose Weight Fast: The Best Drink Recipes for Rapid Results
-

 Education18 hours ago
Education18 hours agoUnlocking the ASUS Student Discount on Reddit: A Comprehensive Guide
-

 News11 hours ago
News11 hours agoUnfiltered: Behind the Headlines with Page Six
-

 Banking15 hours ago
Banking15 hours agoUnlock Your Financial Potential with SoFi High-Yield Savings