Artificial Intelligence
From Algorithms to Sentient Machines: How Artificial Intelligence is Shaping the Future of Every Industry and Daily Life

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as one of the most transformative technologies of the 21st century, profoundly impacting nearly every aspect of human life. From healthcare to finance, transportation to entertainment, AI’s influence is expanding at an unprecedented rate. What began as a concept in the realms of science fiction is now a tangible force driving innovation, economic growth, and societal change.
This article explores the journey of AI from its foundational algorithms to the advent of increasingly autonomous and intelligent systems. We will delve into how AI is revolutionizing industries, enhancing daily life, and raising critical questions about the future of humanity in a world where machines are becoming not just tools, but potentially, sentient partners.
The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence
1. The Origins: From Turing to Neural Networks
The history of AI dates back to the mid-20th century, with British mathematician Alan Turing often credited as the father of modern AI. In 1950, Turing published a seminal paper titled “Computing Machinery and Intelligence,” in which he posed the question, “Can machines think?” He introduced the concept of the Turing Test, a method to evaluate a machine’s ability to exhibit human-like intelligence.
The early days of AI were dominated by rule-based systems and symbolic reasoning, where computers followed predefined rules to solve problems. These systems, known as “Good Old-Fashioned AI” (GOFAI), laid the groundwork for future developments but were limited in their ability to handle complex, real-world tasks.
The 1980s and 1990s saw the rise of neural networks, inspired by the human brain’s structure and functioning. These networks, composed of layers of interconnected nodes (neurons), enabled computers to learn from data through a process called training. However, due to limited computational power and data availability, early neural networks struggled to achieve significant breakthroughs.
2. The AI Renaissance: Big Data, Deep Learning, and Beyond
The AI landscape underwent a dramatic transformation in the early 21st century, driven by the convergence of three key factors: the explosion of big data, advancements in computing power (especially GPUs), and the development of sophisticated algorithms, particularly deep learning.
Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, involves training neural networks with many layers (hence “deep”) on vast amounts of data. This approach has enabled AI systems to achieve remarkable feats in areas such as image recognition, natural language processing, and game playing. For example, in 2012, a deep learning model called AlexNet significantly outperformed previous models in the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge, marking a pivotal moment in AI history.
The advent of deep learning has also fueled the development of AI systems capable of mastering complex games, such as Google DeepMind’s AlphaGo, which defeated the world champion Go player in 2016. These successes have sparked a renewed interest in AI research and development, leading to the proliferation of AI applications across industries.
The Impact of AI Across Industries
AI’s influence extends far beyond research labs and academic papers; it is reshaping industries across the globe. The following sections provide an overview of how AI is transforming key sectors, driving efficiency, innovation, and new business models.
1. Healthcare: Revolutionizing Diagnosis, Treatment, and Care
AI is revolutionizing healthcare by enabling more accurate diagnoses, personalized treatments, and efficient care delivery. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of medical data, identifying patterns that may be invisible to human doctors. This capability is particularly valuable in fields like radiology, where AI systems can detect anomalies in medical images with high accuracy.
One of the most promising applications of AI in healthcare is in predictive analytics. By analyzing patient data, AI can predict the likelihood of diseases, allowing for earlier intervention and better patient outcomes. For instance, AI-powered tools are being used to predict the onset of conditions like diabetes and heart disease, enabling healthcare providers to take preventive measures.
AI is also driving advancements in drug discovery and development. Traditional drug discovery processes are time-consuming and expensive, often taking years to bring a new drug to market. AI algorithms can accelerate this process by analyzing biological data to identify potential drug candidates, reducing both time and cost.
Moreover, AI is enhancing the delivery of healthcare services through telemedicine and virtual health assistants. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide patients with medical advice, appointment scheduling, and medication reminders, improving access to care and reducing the burden on healthcare providers.
2. Finance: Automating Processes and Enhancing Decision-Making
The finance industry has been an early adopter of AI, leveraging its capabilities to automate processes, enhance decision-making, and manage risks. AI-driven algorithms are used in trading, fraud detection, credit scoring, and customer service, among other applications.
In trading, AI-powered systems can analyze market data in real time, identifying trends and making investment decisions faster than any human trader could. These systems, known as algorithmic or high-frequency trading, have become a dominant force in financial markets, accounting for a significant portion of daily trading volume.
Fraud detection is another area where AI excels. Machine learning algorithms can analyze transaction data to identify suspicious activities and flag potential fraud in real time. This capability is particularly important in an era where digital payments and online transactions are increasingly common.
AI is also transforming the way financial institutions interact with customers. Chatbots and virtual assistants are being deployed to handle routine customer inquiries, provide personalized financial advice, and streamline services like loan applications and account management. These AI-powered tools improve customer experience while reducing operational costs.
Moreover, AI is enhancing risk management in finance. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI can identify potential risks and vulnerabilities, enabling financial institutions to take proactive measures to mitigate them. This capability is especially valuable in managing credit risk, market risk, and operational risk.
3. Manufacturing: Driving Efficiency and Innovation
AI is playing a crucial role in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, transforming manufacturing processes and enabling the creation of smart factories. By integrating AI with the Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, and advanced analytics, manufacturers are achieving unprecedented levels of efficiency, productivity, and innovation.
One of the most significant applications of AI in manufacturing is predictive maintenance. AI algorithms can analyze data from sensors embedded in machinery to predict when equipment is likely to fail, allowing for timely maintenance and reducing downtime. This approach not only extends the lifespan of equipment but also minimizes costly disruptions in production.
AI is also enhancing quality control in manufacturing. Computer vision systems powered by AI can inspect products in real time, identifying defects and ensuring that only high-quality goods reach the market. This capability is particularly valuable in industries like automotive and electronics, where precision and quality are paramount.
Moreover, AI is driving innovation in product design and development. Generative design, an AI-powered approach, allows engineers to input design parameters and let the AI generate a range of design options, optimizing for factors like weight, strength, and cost. This approach is enabling the creation of more efficient and innovative products, from aircraft components to consumer electronics.
AI is also facilitating the transition to smart manufacturing, where factories are equipped with interconnected systems that communicate and collaborate autonomously. These smart factories can optimize production processes in real time, respond to changing demands, and even reconfigure themselves to produce different products, offering manufacturers greater flexibility and agility.
4. Transportation: The Journey Toward Autonomous Vehicles
The transportation industry is undergoing a radical transformation, with AI at the forefront of innovations that promise to change how we move people and goods. The most high-profile application of AI in transportation is the development of autonomous vehicles, which have the potential to revolutionize mobility.
Autonomous vehicles rely on AI algorithms to process data from sensors, cameras, and lidar systems, enabling them to perceive their environment, make decisions, and navigate safely. Companies like Tesla, Waymo, and Uber are leading the charge in developing self-driving cars, with varying levels of autonomy already being tested and deployed.
The benefits of autonomous vehicles are manifold. They have the potential to reduce traffic accidents, as AI systems can react faster and more accurately than human drivers. Autonomous vehicles could also improve traffic flow, reduce congestion, and lower emissions by optimizing routes and driving patterns.
AI is also transforming logistics and supply chain management. AI-powered systems can optimize routing and scheduling for delivery trucks, reducing fuel consumption and improving efficiency. In warehouses, AI-driven robots are being used to automate tasks like picking, packing, and inventory management, speeding up operations and reducing labor costs.
Moreover, AI is enabling the development of smart transportation systems that integrate with urban infrastructure to manage traffic, monitor road conditions, and enhance public transportation services. These systems use AI to analyze data from various sources, making real-time adjustments to improve the overall efficiency and safety of transportation networks.
5. Retail: Personalization and Customer Experience
The retail industry is leveraging AI to enhance customer experience, streamline operations, and drive sales. AI-powered technologies are enabling retailers to offer personalized shopping experiences, optimize inventory management, and automate customer service.
Personalization is a key area where AI is making a significant impact. By analyzing customer data, AI algorithms can predict individual preferences and recommend products tailored to each shopper’s tastes. This level of personalization extends to online shopping, where AI-driven recommendation engines suggest products based on browsing history, purchase behavior, and even social media activity.
In physical stores, AI is being used to enhance the shopping experience through smart shelves, which use sensors and AI to track inventory levels and provide real-time product information to shoppers. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are also being deployed to assist customers, answer questions, and provide personalized recommendations, both online and in-store.
AI is also optimizing supply chain management in retail. Machine learning algorithms can predict demand patterns, allowing retailers to manage inventory more efficiently and reduce waste. AI-driven analytics are also being used to optimize pricing strategies, ensuring that products are priced competitively while maximizing profits.
Moreover, AI is transforming the way retailers interact with customers through augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) applications. These technologies, powered by AI, allow customers to virtually try on clothes, visualize furniture in their homes, and explore products in immersive environments, enhancing the shopping experience and driving sales.
AI in Daily Life: Enhancing Convenience and Connectivity
AI is not just transforming industries; it is also becoming an integral part of our daily lives, enhancing convenience, connectivity, and entertainment. From smart homes to virtual assistants, AI is reshaping how we interact with technology and each other.
1. Smart Homes: AI-Powered Convenience and Efficiency
The concept of the smart home has evolved rapidly, with AI at its core. AI-powered devices and systems are making homes more convenient, efficient, and secure, offering a level of automation and control that was once the stuff of science fiction.
Smart home assistants like Amazon’s Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri are among the most visible AI applications in daily life. These virtual assistants use natural language processing and machine learning to understand voice commands, answer questions, control smart home devices, and even provide personalized recommendations.
AI is also driving the automation of home systems, from lighting and climate control to security and entertainment. Smart thermostats, like those from Nest, learn users’ preferences and adjust heating and cooling systems accordingly, optimizing energy usage and reducing costs. Smart lighting systems can be programmed to adjust brightness and color based on the time of day or activity, enhancing comfort and ambiance.
Home security has also been enhanced by AI-powered devices, such as smart cameras and doorbells, which use computer vision to recognize faces and detect unusual activity. These systems can alert homeowners to potential security threats in real time, offering peace of mind and greater control over home safety.
Moreover, AI is being integrated into home appliances, from refrigerators that track inventory and suggest recipes to washing machines that optimize water and detergent usage based on the load. These smart appliances not only make household chores easier but also contribute to greater energy efficiency and sustainability.
2. Virtual Assistants and Personalization
Virtual assistants are becoming ubiquitous, not just in homes but also on our smartphones, cars, and wearable devices. These AI-powered assistants are transforming the way we interact with technology, providing personalized experiences that are tailored to our preferences and habits.
On smartphones, virtual assistants like Siri, Google Assistant, and Bixby can perform a wide range of tasks, from setting reminders and sending messages to searching the web and providing directions. These assistants use AI to learn from user interactions, becoming more accurate and responsive over time.
In cars, AI-powered infotainment systems are enhancing the driving experience by providing navigation, entertainment, and hands-free communication. These systems can learn drivers’ preferences, such as favorite routes and music, and provide personalized recommendations.
Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, are also leveraging AI to provide personalized health and fitness insights. These devices use AI to analyze data on physical activity, sleep patterns, and vital signs, offering personalized recommendations for improving health and well-being.
Moreover, AI is driving the personalization of online experiences, from social media feeds to content recommendations. Algorithms analyze user behavior to curate content that aligns with individual interests, making online experiences more engaging and relevant.
3. Entertainment: AI in Gaming, Music, and Film
AI is revolutionizing the entertainment industry, enabling the creation of more immersive and interactive experiences in gaming, music, and film. AI-powered tools are being used to enhance creativity, improve content delivery, and provide personalized entertainment.
In gaming, AI is driving the development of more intelligent and adaptive non-player characters (NPCs) that can interact with players in more realistic and engaging ways. AI is also being used to create procedurally generated content, such as levels, maps, and narratives, allowing for infinite variations and replayability.
AI is also transforming music production and recommendation. AI-powered tools can analyze musical patterns and generate new compositions, assisting musicians in the creative process. Streaming platforms like Spotify use AI to recommend songs and playlists based on user preferences, creating a personalized listening experience.
In the film industry, AI is being used to enhance visual effects, edit footage, and even create entirely new scenes through techniques like deepfake technology. AI is also playing a role in content recommendation, with streaming services like Netflix using AI to analyze viewer behavior and suggest movies and TV shows that align with individual tastes.
The Ethical Implications of AI: Challenges and Considerations
As AI becomes more pervasive, it raises important ethical questions and challenges that society must address. The potential for AI to influence decision-making, privacy, and employment highlights the need for careful consideration of the implications of AI technologies.
1. Bias and Fairness
AI systems are only as good as the data they are trained on. If the training data contains biases, the AI system may perpetuate or even exacerbate those biases in its decision-making processes. This issue has significant implications, particularly in areas like hiring, law enforcement, and lending, where biased AI could lead to unfair outcomes.
Ensuring fairness in AI requires careful design, testing, and monitoring of algorithms to identify and mitigate biases. This challenge underscores the importance of diversity in AI development teams and the need for transparent, explainable AI systems that can be audited for fairness.
2. Privacy and Surveillance
The widespread use of AI in data collection and analysis raises concerns about privacy and surveillance. AI systems can analyze vast amounts of personal data, from online behavior to biometric information, potentially infringing on individual privacy rights.
There is also the risk of AI being used for mass surveillance, with governments and corporations leveraging AI to monitor and track individuals on an unprecedented scale. Balancing the benefits of AI with the need to protect privacy and civil liberties is a critical challenge that requires robust legal and regulatory frameworks.
3. Employment and the Future of Work
AI’s ability to automate tasks and processes has raised concerns about the impact on employment, particularly in industries where routine jobs are at risk of being replaced by machines. While AI can create new opportunities and roles, there is a real risk of job displacement, particularly for workers in low-skill, repetitive jobs.
Addressing this challenge requires a proactive approach, including retraining and reskilling workers, promoting lifelong learning, and ensuring that the benefits of AI-driven productivity gains are shared broadly across society.
4. Autonomy and Control
As AI systems become more autonomous, questions arise about control and accountability. Who is responsible when an AI system makes a mistake or causes harm? How do we ensure that AI systems act in ways that align with human values and interests?
These questions highlight the need for clear guidelines and regulations governing the development and deployment of AI, as well as ongoing research into the ethical implications of increasingly autonomous systems.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is undeniably reshaping the world as we know it, driving innovation, efficiency, and personalization across industries and daily life. From healthcare to finance, manufacturing to transportation, AI is transforming how we live, work, and interact with the world around us.
However, the rapid advancement of AI also brings significant ethical challenges and considerations. As AI continues to evolve, it is crucial that society addresses these challenges, ensuring that AI is developed and deployed in ways that are fair, transparent, and aligned with human values.
The future of AI holds immense potential, with the promise of even more sophisticated and autonomous systems on the horizon. As we navigate this rapidly changing landscape, it is essential to strike a balance between embracing the opportunities that AI offers and addressing the ethical implications that come with it.
In the end, the story of AI is not just about machines becoming smarter; it is about how we, as a society, choose to shape the future of this powerful technology and its role in our lives. Whether AI becomes a tool for enhancing human potential or a force that exacerbates existing inequalities will depend on the choices we make today.
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoBellarium ($BEL) Price Prediction: Could It Hit $5 by 2026?
-
 Press Release2 days ago
Press Release2 days agoClinical Trials Market Set for Robust Growth, Driven by Drug Development Surge and Digital Innovation
-

 Press Release3 days ago
Press Release3 days agoIndustrial Boiler Market Expected to Surpass USD 24.4 Billion by 2035 Amid Growing Demand for Energy Efficiency and Industrialization
-
 Press Release3 days ago
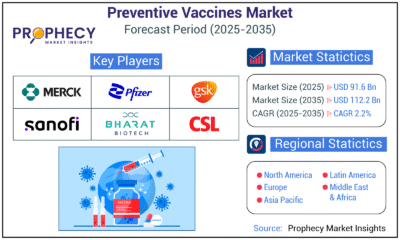
Press Release3 days agoPreventive Vaccines Market to Witness Strong Growth by 2035
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoHow Managed IT Solutions Help Small Teams Compete at Enterprise Scale
-

 Press Release3 days ago
Press Release3 days agoGreen Bio Chemicals Market Poised for Sustainable Growth amidst Global Shift to Eco-Friendly Alternatives by 2035
-

 Press Release3 days ago
Press Release3 days agoFill-Finish Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Market Expected to Flourish Amid Biopharmaceutical Boom and Global Outsourcing Trend by 2035
-

 Press Release3 days ago
Press Release3 days agoPet Food Nutraceutical Market Set for Robust Expansion Amid Rising Demand for Pet Wellness by 2035