Automotive
Automotive Supply Chain Management: Trends and Challenges

The automotive supply chain is a vital part of the industry, connecting various suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors around the globe. As we navigate through a rapidly changing landscape, it is essential to understand the latest trends and the challenges that lie ahead. This article explores key trends in automotive supply chain management and the obstacles faced by the industry, providing insights into how companies can adapt and thrive in this complex environment.
Key Takeaways
- Automotive supply chains are increasingly complex, often involving thousands of parts sourced globally.
- Geopolitical issues, such as trade disputes and political unrest, can disrupt supply chains significantly.
- Raw material shortages pose a serious threat to production, affecting costs and timelines.
- Technological advancements, including electric vehicles and automation, are reshaping supply chain strategies.
- Labour shortages and an ageing workforce highlight the need for new skills and training in the automotive sector.
Current Trends in Automotive Supply Chain Management
Just-in-Time and Just-in-Sequence Production
The automotive industry is increasingly adopting Just-in-Time (JIT) and Just-in-Sequence (JIS) production methods. These strategies help reduce waste and improve efficiency by ensuring that parts arrive exactly when needed. This approach not only cuts costs but also enhances flexibility in production schedules.
Global Sourcing and Supplier Diversity
Global sourcing is becoming essential for automotive manufacturers. By diversifying their supplier base, companies can mitigate risks associated with relying on a single source. This trend allows for better negotiation power and access to a wider range of materials and components. Key benefits include:
- Cost savings through competitive pricing
- Increased innovation from diverse suppliers
- Risk management by avoiding supply disruptions
Technological Integration and Automation
The integration of technology in supply chains is transforming the automotive sector. Automation and advanced technologies, such as AI and IoT, are streamlining operations and enhancing productivity. Real-time data allows manufacturers to make informed decisions quickly, improving overall supply chain performance.
The automotive industry must embrace these trends to remain competitive and responsive to market demands.
| Trend | Description | Impact on Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Just-in-Time Production | Reduces waste and improves efficiency | Lower costs, increased flexibility |
| Global Sourcing | Diversifies supplier base | Better negotiation power |
| Technological Integration | Enhances productivity through automation | Improved decision-making |
In summary, the automotive supply chain is evolving rapidly, driven by the need for efficiency, diversity, and technological advancement. Companies that adapt to these trends will be better positioned to face future challenges and meet consumer demands effectively.
Impact of Geopolitical Instability on Automotive Supply Chains
Geopolitical instability can have a significant impact on automotive supply chains, affecting everything from production to delivery. The automotive industry relies on a complex network of suppliers and manufacturers across the globe, making it vulnerable to disruptions caused by political tensions.
Trade Wars and Tariffs
Trade wars, such as the US-China trade conflict, have led to increased tariffs on automotive components. This has forced manufacturers to rethink their supply chain strategies. Key points include:
- Higher costs for imported parts.
- Need to find alternative suppliers.
- Potential delays in production schedules.
Political Instability in Key Regions
Political unrest in regions that are crucial for automotive production can disrupt the supply chain. For example:
- Factory shutdowns due to protests.
- Logistical challenges in transporting goods.
- Increased risk of supply shortages.
Strategies for Mitigating Geopolitical Risks
To navigate these challenges, companies can adopt several strategies:
- Diversifying suppliers to reduce dependency on any single region.
- Investing in local production to minimise import risks.
- Enhancing communication with suppliers to stay informed about potential disruptions.
The automotive industry must remain agile and adaptable to survive in a world where geopolitical tensions are ever-present.
In summary, geopolitical instability poses serious challenges to automotive supply chains, but with proactive strategies, companies can mitigate these risks and maintain operational efficiency. Ongoing geopolitical developments will continue to shape the future of the automotive supply chain.
Challenges of Raw Material Shortages
The automotive industry is heavily dependent on a consistent supply of raw materials like steel, aluminium, and rare earth metals. However, shortages of these materials can lead to significant production disruptions. Here are some key factors contributing to these shortages:
Factors Contributing to Shortages
- Increased demand from other industries, such as electronics and construction.
- Geopolitical tensions affecting mining regions, which can limit access to essential materials.
- Environmental regulations that restrict extraction activities, making it harder to source materials.
Impact on Production and Costs
The impact of raw material shortages can be severe:
- Production delays due to the inability to source necessary components.
- Increased costs as manufacturers compete for limited supplies.
- Reduced output, which can lead to lost sales and market share.
Strategies for Managing Raw Material Supply
To tackle these challenges, automotive manufacturers can consider the following strategies:
- Diversifying suppliers to reduce reliance on single sources.
- Investing in recycling to reclaim materials from old vehicles.
- Building strategic reserves of critical materials to buffer against shortages.
The automotive sector must adapt to these challenges to ensure a stable supply chain and maintain production efficiency. Addressing raw material shortages is crucial for long-term sustainability.
Technological Advancements and Their Effects on Supply Chains
Shift Towards Electric Vehicles
The automotive industry is undergoing a significant transformation with the shift towards electric vehicles (EVs). This change requires new supply chains for batteries and other components. Manufacturers must adapt to these new demands, which can be complex and costly.
Integration of Autonomous Driving Technologies
The rise of autonomous driving technologies is also reshaping supply chains. Companies need to source advanced sensors and software, which adds layers of complexity to logistics and production processes. This integration can lead to increased costs and necessitates a reevaluation of existing supply chain strategies.
Adoption of Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
The adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies such as automation and artificial intelligence is crucial for improving efficiency. These technologies can streamline operations, but they also require skilled workers who understand how to use them effectively.
Key Points to Consider:
- Investment in Technology: Embracing new technologies can enhance supply chain visibility and efficiency.
- Training Workforce: Developing skills in the workforce is essential to manage these advanced technologies.
- Collaboration with Suppliers: Strong partnerships with suppliers can facilitate smoother transitions to new technologies.
The automotive industry must continuously innovate to keep pace with technological advancements, ensuring that supply chains remain efficient and resilient.
| Technology Type | Impact on Supply Chain | Challenges Faced |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Vehicles | New sourcing requirements | High initial costs |
| Autonomous Driving Technologies | Increased complexity in logistics | Need for skilled workforce |
| Advanced Manufacturing | Improved efficiency and productivity | Integration with existing systems |
Labour Shortages and Skills Gap in the Automotive Industry
High Turnover Rates
The automotive industry is currently facing significant labour turnover issues. Many workers are leaving their jobs, which creates a gap in skilled labour. This situation is worsened by a lack of proper training and development opportunities within companies. To tackle this, businesses need to:
- Offer ongoing training programmes.
- Create a positive work environment.
- Regularly check in with employees to understand their needs.
Ageing Workforce
Another challenge is the ageing workforce. Many experienced workers are retiring, and there aren’t enough young people entering the industry to replace them. This leads to a shortage of skilled workers who can handle advanced technologies. Companies must:
- Promote careers in the automotive sector to younger generations.
- Partner with educational institutions to develop relevant training programmes.
- Highlight the benefits of working in the automotive industry.
Need for New Skill Sets
As the industry evolves, there is a growing need for new skill sets. With the rise of electric vehicles and automation, workers must be trained in new technologies. This requires:
- Updating training programmes to include new technologies.
- Encouraging continuous learning and development.
- Collaborating with tech companies to provide the necessary skills.
The automotive industry must adapt to these challenges to ensure a skilled workforce for the future. Investing in training and development is crucial for maintaining productivity and innovation.
Regulatory Compliance and Sustainability
Navigating Safety and Emissions Regulations
The automotive industry faces a complex set of safety and emissions regulations that manufacturers must comply with. This often requires significant changes in production processes and supply chain management. Key points include:
- Understanding local and international regulations.
- Regular audits to ensure compliance.
- Training staff on regulatory requirements.
Adopting Sustainable Practises
To meet growing environmental concerns, automotive companies are increasingly adopting sustainable practises. This includes:
- Using alternative fuels and energy sources.
- Developing low-emission vehicles.
- Implementing recycling and circular economy principles.
Challenges in Implementing Eco-Friendly Supply Chains
Despite the push for sustainability, there are challenges in creating eco-friendly supply chains. These challenges include:
- High costs associated with sustainable materials.
- Difficulty in sourcing compliant suppliers.
- Need for advanced technology to track sustainability metrics.
The automotive industry is under pressure to reduce its ecological footprint while maintaining efficiency and profitability. Strategic partnerships and innovative technologies are essential for achieving these goals.
| Challenge | Impact on Supply Chain | Potential Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| High costs of sustainable materials | Increased production costs | Seek government subsidies |
| Difficulty in sourcing suppliers | Delays in production | Develop local supplier networks |
| Tracking sustainability metrics | Lack of transparency | Implement advanced tracking systems |
Natural Disasters and Environmental Factors
Natural disasters, like earthquakes and floods, can severely disrupt automotive supply chains. For instance, the 2011 earthquake and tsunami in Japan caused major delays in the supply of essential automotive parts, affecting production globally. Moreover, environmental issues such as climate change are making these disasters more frequent and intense, which poses a significant risk to supply chain stability.
Impact of Natural Disasters on Supply Chains
- Production Halts: Natural disasters can lead to immediate shutdowns of factories.
- Supply Shortages: Key components may become unavailable, leading to delays.
- Increased Costs: Companies may face higher costs due to emergency measures and sourcing alternatives.
Climate Change and Increased Frequency of Disasters
The effects of climate change are evident, with rising temperatures and unpredictable weather patterns leading to more frequent natural disasters. This trend can disrupt supply chains in several ways:
- Infrastructure Damage: Roads and ports may be damaged, hindering transportation.
- Resource Scarcity: Essential materials may become harder to obtain.
- Regulatory Changes: New laws may emerge to address environmental concerns, impacting operations.
Strategies for Enhancing Supply Chain Resilience
To better prepare for these challenges, companies can adopt several strategies:
- Diversification of Suppliers: Relying on multiple suppliers can reduce risks.
- Investment in Technology: Using advanced technologies can improve monitoring and response times.
- Emergency Planning: Having a solid plan in place can help companies react quickly to disasters.
In summary, the automotive industry must adapt to the growing threat of natural disasters and environmental factors. By implementing effective strategies, companies can enhance their resilience and ensure smoother operations in the face of adversity.
Pandemic-Related Disruptions in Automotive Supply Chains

Factory Shutdowns and Labour Shortages
The COVID-19 pandemic exposed the fragility of global supply chains. Many factories had to shut down temporarily, leading to significant production delays. Labour shortages also became a major issue as workers fell ill or were unable to commute. This situation resulted in a backlog of orders and increased pressure on remaining staff.
Logistical Challenges During Pandemics
Logistics faced severe disruptions during the pandemic. Shipping routes were affected, causing delays in the delivery of essential parts. Here are some key logistical challenges:
- Port congestion due to reduced workforce and increased safety measures.
- Shipping delays from lockdowns in various countries.
- Increased transportation costs as demand for shipping surged.
Shifts in Consumer Demand
The pandemic changed how people viewed transportation. With more individuals working from home, there was a sudden rise in demand for personal vehicles. This shift strained supply chains that were already struggling with production halts. Manufacturers had to adapt quickly to meet this new demand, which often meant prioritising certain models over others.
The pandemic has taught us that flexibility and resilience in supply chains are crucial for navigating unexpected challenges.
In summary, the automotive industry faced numerous hurdles during the pandemic, from factory shutdowns to shifts in consumer behaviour. These challenges highlighted the need for better planning and adaptability in supply chain management.
Enhancing Supply Chain Visibility and Transparency
In today’s automotive industry, enhancing visibility and transparency in supply chains is crucial for success. Companies are increasingly adopting technologies that provide real-time insights into their operations. This shift not only improves efficiency but also strengthens relationships with suppliers and customers.
Importance of Real-Time Insights
- Quick Decision-Making: Access to real-time data allows companies to make informed decisions swiftly.
- Improved Collaboration: Enhanced visibility fosters better communication between partners, leading to stronger relationships.
- Risk Management: Identifying potential disruptions early helps in mitigating risks effectively.
Technologies for Improving Transparency
- Cloud-Based Solutions: These platforms enable easy access to data across the supply chain, making it simpler to track materials and shipments.
- Dashboards: Visual tools that present key metrics at a glance, helping teams monitor performance and identify issues.
- EDI (Electronic Data Interchange): Streamlines communication and data exchange between partners, reducing errors and delays.
Challenges in Achieving Full Visibility
- Data Silos: Different systems may not communicate well, leading to gaps in information.
- Complex Supply Chains: The more complex the supply chain, the harder it is to maintain visibility.
- Resistance to Change: Some organisations may be hesitant to adopt new technologies or processes.
To thrive in the competitive automotive landscape, companies must prioritise visibility and transparency in their supply chains. This commitment not only enhances operational efficiency but also builds trust with partners and customers alike.
By focusing on these areas, businesses can navigate the complexities of the automotive supply chain more effectively, ensuring they remain agile and responsive to market demands.
Logistical Challenges in the Automotive Sector

Port Congestion and Shipping Delays
The automotive industry is currently grappling with port congestion and shipping delays, which have become significant hurdles. These issues arise from:
- Increased global demand for vehicles.
- Limited shipping capacity due to pandemic-related restrictions.
- Inefficiencies in port operations.
Transportation Costs and Efficiency
Rising transportation costs are impacting the overall efficiency of automotive logistics. Factors contributing to this include:
- Fluctuating fuel prices.
- Increased demand for freight services.
- Regulatory changes affecting transportation routes.
Impact of Just-in-Time Inventory Systems
The reliance on just-in-time inventory systems has made the automotive supply chain more vulnerable. While this approach reduces inventory costs, it also means that any disruption can lead to:
- Production halts.
- Increased lead times for parts.
- Higher costs due to expedited shipping.
The automotive sector must adapt to these logistical challenges to maintain efficiency and meet consumer demands. Recent events have highlighted the vulnerabilities in the automotive industry’s global supply chains.
Future Outlook for Automotive Supply Chain Management
Emerging Trends and Innovations
The automotive supply chain is evolving rapidly, driven by new technologies and changing consumer demands. Companies are increasingly focusing on:
- Sustainability: Reducing environmental impact through eco-friendly practises.
- Digital Transformation: Implementing advanced technologies for better efficiency.
- Diversity in Sourcing: Expanding supplier networks to mitigate risks.
Long-Term Strategies for Stability
To ensure stability in the face of ongoing challenges, automotive manufacturers should consider:
- Investing in Technology: Embracing automation and data analytics.
- Building Resilience: Developing flexible supply chains that can adapt to disruptions.
- Enhancing Collaboration: Strengthening partnerships with suppliers for better communication.
Role of Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is crucial for the future of automotive supply chains. It enables:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Keeping track of inventory and logistics.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Using analytics to improve efficiency.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Meeting consumer demands more effectively.
The future of automotive supply chains will depend on the ability to adapt to rapid changes and embrace innovative solutions.
| Trend | Impact on Supply Chain |
|---|---|
| Sustainability | Reduces environmental footprint |
| Digital Transformation | Increases efficiency and transparency |
| Supplier Diversity | Mitigates risks and enhances resilience |
Conclusion
In summary, the automotive supply chain is facing many difficulties that affect its smooth operation. Issues like shortages of materials, rising costs, and the need for skilled workers are just a few of the challenges that manufacturers must tackle. As the industry shifts towards electric vehicles and new technologies, it is crucial for companies to adapt and find innovative solutions. By focusing on improving communication, investing in training, and embracing sustainable practises, the automotive sector can work towards a more stable and efficient future. Addressing these challenges will not only help manufacturers but also ensure that customers receive the vehicles they need in a timely manner.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main challenges in the automotive supply chain?
The automotive supply chain faces many challenges, such as managing thousands of parts, sourcing materials from different countries, and dealing with shortages of important components like microchips. These issues can cause delays and increase costs.
How does geopolitical instability affect automotive supply chains?
Geopolitical issues, like trade disputes and political unrest, can disrupt the flow of parts and materials. This can lead to higher costs and delays in production, making it hard for manufacturers to keep up with demand.
What are raw material shortages, and why are they a problem?
Raw material shortages happen when there isn’t enough of essential materials like steel or aluminium. This can slow down production and raise costs, affecting the overall supply chain.
How is technology changing automotive supply chains?
Technology is making supply chains smarter and more efficient. For example, the rise of electric vehicles needs new parts and processes, which can complicate things but also improve efficiency.
Why is there a skills gap in the automotive industry?
The automotive industry is facing a skills gap because there aren’t enough trained workers to meet the demand. Many workers are retiring, and new technologies require different skills that current employees may not have.
What do manufacturers need to do to comply with regulations?
Manufacturers must follow various rules about safety and emissions. This often means changing their processes and materials, which can be challenging and costly.
How do natural disasters impact automotive supply chains?
Natural disasters can halt production by damaging facilities or disrupting transport routes. This can lead to significant delays and increased costs for manufacturers.
What lessons did the automotive industry learn from the COVID-19 pandemic?
The pandemic showed how fragile supply chains can be. Many manufacturers learned the importance of having backup plans and diversifying their suppliers to avoid future disruptions.
-

 Press Release6 days ago
Press Release6 days agoBellarium ($BEL) Price Prediction: Could It Hit $5 by 2026?
-
 Press Release3 days ago
Press Release3 days agoClinical Trials Market Set for Robust Growth, Driven by Drug Development Surge and Digital Innovation
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoHow Managed IT Solutions Help Small Teams Compete at Enterprise Scale
-

 Press Release4 days ago
Press Release4 days agoIndustrial Boiler Market Expected to Surpass USD 24.4 Billion by 2035 Amid Growing Demand for Energy Efficiency and Industrialization
-

 Press Release4 days ago
Press Release4 days agoFill-Finish Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Market Expected to Flourish Amid Biopharmaceutical Boom and Global Outsourcing Trend by 2035
-
 Press Release4 days ago
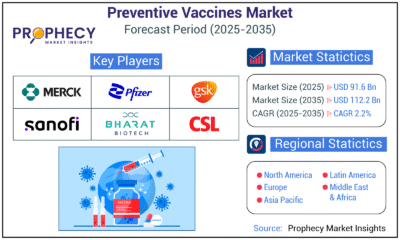
Press Release4 days agoPreventive Vaccines Market to Witness Strong Growth by 2035
-

 Press Release4 days ago
Press Release4 days agoGreen Bio Chemicals Market Poised for Sustainable Growth amidst Global Shift to Eco-Friendly Alternatives by 2035
-

 Press Release4 days ago
Press Release4 days agoPet Food Nutraceutical Market Set for Robust Expansion Amid Rising Demand for Pet Wellness by 2035