Automotive
Automotive Cybersecurity Solutions: Protecting Your Ride

As cars become smarter and more connected, the importance of automotive cybersecurity has never been greater. This article explores various aspects of protecting vehicles from cyber threats, including common types of attacks, innovative technologies, and best practises for vehicle owners. With the rise of connected cars, understanding how to safeguard these vehicles is essential for safety and security on the road.
Key Takeaways
- Automotive cybersecurity is essential for protecting connected vehicles from cyber threats.
- Common threats include hacking into vehicle systems and exploiting software vulnerabilities.
- Vehicle owners should regularly update software and be cautious with third-party apps.
- Innovative technologies like AI and blockchain are being used to enhance automotive security.
- Regulatory compliance is crucial for manufacturers to ensure the safety of connected vehicles.
Understanding Automotive Cybersecurity Solutions
Definition and Importance
Automotive cybersecurity refers to the measures taken to protect vehicles from cyber threats. As vehicles become more connected, the need for robust cybersecurity solutions is crucial. These solutions help safeguard not just the vehicle but also the safety of its passengers.
Key Components
Key components of automotive cybersecurity include:
- Network Security: Protecting communication networks within the vehicle.
- Data Protection: Ensuring that sensitive information is secure from breaches.
- Software Integrity: Regular updates and checks to maintain software security.
| Component | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Network Security | Protects vehicle communication networks | Prevents unauthorised access |
| Data Protection | Safeguards sensitive information | Protects personal data |
| Software Integrity | Ensures software is up-to-date and secure | Reduces vulnerabilities |
Current Trends
The automotive industry is witnessing several trends in cybersecurity:
- Increased Connectivity: More vehicles are connected to the internet, increasing potential attack surfaces.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stricter regulations are being introduced to ensure vehicle safety.
- Emerging Technologies: Innovations like AI and machine learning are being used to enhance security measures.
As vehicles evolve, so must our approach to cybersecurity. It is essential to stay ahead of potential threats to ensure safety and security in the automotive world.
Common Cyber Threats to Modern Vehicles
Types of Cyber Attacks
Modern vehicles face various cyber threats, including:
- Remote Hacking: Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in vehicle software to gain control from afar.
- Physical Access: If someone can physically access the vehicle, they can manipulate its systems directly.
- Malware: Malicious software can be introduced through unsecured connections, affecting vehicle performance.
Real-World Examples
Several incidents highlight the risks:
- Jeep Hack: In 2015, hackers remotely took control of a Jeep, leading to a massive recall of 1.4 million vehicles.
- Tesla Breach: Cybercriminals attempted to extort Tesla by infiltrating its systems, showcasing the need for robust security.
- Toyota Incident: A vulnerability in Toyota’s software allowed hackers to access sensitive data, raising alarms in the industry.
Impact on Vehicle Safety
The consequences of cyber attacks can be severe:
- Loss of Control: Hackers can take over vehicle functions, posing a danger to drivers and passengers.
- Data Theft: Personal information can be stolen, leading to identity theft and financial loss.
- Reputation Damage: Manufacturers may suffer significant reputational harm, affecting consumer trust.
As vehicles become more connected, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. Protecting against these threats is essential for ensuring safety and trust in modern automotive technology.
Protecting Vehicle Communication Networks
V2V and V2X Communications
Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) and Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communications are essential for modern automotive technology. These systems allow vehicles to share information with each other and with infrastructure, enhancing safety and efficiency. Effective communication is crucial to prevent accidents and improve traffic flow.
Encryption Techniques
To safeguard these communications, encryption techniques are vital. Here are some key methods:
- Symmetric Encryption: Uses the same key for both encryption and decryption, ensuring that only authorised parties can access the data.
- Asymmetric Encryption: Involves a pair of keys (public and private) to secure communications, making it harder for attackers to intercept data.
- Hashing: Converts data into a fixed-size string of characters, which helps verify data integrity without revealing the original data.
Regulatory Standards
Regulatory standards play a significant role in ensuring the security of vehicle communication networks. Key standards include:
- UNECE WP29 Regulations: Mandate cybersecurity measures for vehicles sold in Europe.
- ISO SEA 21434 Standards: Provide guidelines for cybersecurity in road vehicles.
- NHTSA Guidelines: Offer best practises for manufacturers to follow in the U.S.
Protecting vehicle communication networks is not just about technology; it’s about ensuring the safety of everyone on the road. By adhering to regulations and employing robust encryption techniques, we can significantly reduce the risk of cyber threats.
Securing In-Vehicle Systems and Software

Electronic Control Units (ECUs)
Modern vehicles are equipped with numerous Electronic Control Units (ECUs) that manage various functions, from engine control to infotainment. These units are crucial for vehicle performance but can also be vulnerable to cyber threats. To secure ECUs, manufacturers must:
- Implement strong authentication methods.
- Regularly update software to patch vulnerabilities.
- Monitor ECU communications for unusual activity.
Infotainment Systems
Infotainment systems provide entertainment and navigation but can be entry points for cyber attacks. To protect these systems, it is essential to:
- Use secure coding practises during development.
- Limit access to sensitive data.
- Regularly update the system to fix security flaws.
Over-the-Air Updates
Over-the-Air (OTA) updates allow manufacturers to remotely update vehicle software, enhancing security and functionality. However, these updates must be secure to prevent malicious interference. Key practises include:
- Encrypting update files to prevent tampering.
- Verifying the authenticity of updates before installation.
- Providing clear communication to users about updates.
Protecting in-vehicle systems is not just about technology; it’s about ensuring the safety and trust of vehicle owners. Regular updates and monitoring are essential.
By focusing on these areas, the automotive industry can significantly enhance the security of in-vehicle systems and software, ensuring a safer driving experience for everyone.
The Role of OEMs in Automotive Cybersecurity
Partnerships with Cybersecurity Firms
Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) are increasingly recognising the need for strong partnerships with cybersecurity firms. These collaborations help in:
- Developing advanced security solutions.
- Sharing knowledge and expertise.
- Enhancing overall vehicle safety.
In-House Security Measures
OEMs are also focusing on building their own security measures. This includes:
- Implementing robust security protocols during vehicle design.
- Conducting regular security audits and assessments.
- Training staff on cybersecurity best practises.
Compliance with Regulations
To ensure safety, OEMs must comply with various regulations. Key standards include:
- UNECE WP29 R155: Requires OEMs to demonstrate cybersecurity measures.
- ISO 21434: Provides a framework for integrating cybersecurity into vehicle development.
OEMs play a crucial role in safeguarding vehicles against cyber threats, ensuring that both the technology and the consumer’s safety are prioritised throughout the vehicle’s lifecycle.
By adhering to these practises, OEMs not only protect their vehicles but also build trust with consumers, ensuring a safer driving experience.
Best Practises for Vehicle Owners
Regular Software Updates
Keeping your vehicle’s software up to date is crucial. Manufacturers often release updates that fix security issues and improve performance. Make it a habit to check for updates regularly.
Safe Use of Third-Party Apps
When using apps in your car, always choose reputable sources. Avoid installing apps that seem suspicious or come from unknown developers. This helps protect your vehicle from potential threats.
Monitoring for Unusual Activity
Stay alert for any strange behaviour in your vehicle. If you notice anything unusual, such as unexpected alerts or changes in performance, investigate immediately. This can help you catch potential cyber threats early.
| Best Practise | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Software Updates | Check for and install updates frequently to patch vulnerabilities. |
| Safe Use of Third-Party Apps | Only use trusted apps to reduce the risk of malware. |
| Monitoring for Unusual Activity | Be vigilant about any odd behaviour in your vehicle. |
As vehicles are expected to operate for over 20 years, they must be designed to withstand emerging threats and maintain cybersecurity throughout their life cycle.
By following these best practises, you can significantly enhance the security of your connected car and enjoy a safer driving experience.
Innovative Cybersecurity Technologies
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming automotive cybersecurity. These technologies can analyse vast amounts of data to identify patterns and detect anomalies that may indicate a cyber threat. AI-driven systems can respond to threats in real-time, making them essential for modern vehicles.
Blockchain Applications
Blockchain technology offers a secure way to manage vehicle data. By creating a tamper-proof ledger, it ensures that all communications and transactions are recorded securely. This can help in verifying the authenticity of software updates and protecting against data breaches.
Advanced Threat Detection Systems
Advanced threat detection systems use sophisticated algorithms to monitor vehicle networks continuously. They can identify potential threats before they cause harm. Here are some key features of these systems:
- Real-time monitoring of vehicle systems
- Automated alerts for suspicious activities
- Integration with existing security protocols
In the rapidly evolving world of automotive technology, staying ahead of cyber threats is crucial for ensuring safety and security.
| Technology Type | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| AI and ML | Real-time threat detection |
| Blockchain | Secure data management |
| Advanced Threat Detection | Continuous monitoring and alerts |
These innovative technologies are paving the way for a safer driving experience, ensuring that vehicles remain protected against emerging cyber threats. As companies like Upstream Security lead the charge with their cloud-enabled applications, the future of automotive cybersecurity looks promising.
Case Studies of Leading Cybersecurity Solutions

HARMAN SHIELD
HARMAN SHIELD is a key player in automotive cybersecurity, providing solutions that monitor the cyber posture of connected vehicles. This system uses various data sources, including operational telematics and in-vehicle cybersecurity components, to ensure safety and security.
Argus Cyber Security
Argus focuses on protecting vehicles from cyber threats through its innovative solutions. Their technology is designed to secure vehicle communication networks and detect potential threats in real-time. This proactive approach helps in maintaining the integrity of vehicle systems.
GuardKnox
GuardKnox offers a unique approach by integrating cybersecurity directly into the vehicle’s architecture. Their solutions are tailored to protect against both external and internal threats, ensuring that vehicles remain safe from cyber attacks. They emphasise the importance of in-vehicle security to safeguard sensitive data and systems.
| Company | Key Features | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|
| HARMAN SHIELD | Cyber posture monitoring, data source integration | OEMs, automotive manufacturers |
| Argus Cyber Security | Real-time threat detection, network protection | Vehicle manufacturers, fleet operators |
| GuardKnox | In-vehicle architecture security, internal threat protection | Automotive OEMs, tech developers |
The automotive industry is rapidly evolving, and with it, the need for robust cybersecurity solutions is becoming increasingly critical. Companies like HARMAN, Argus, and GuardKnox are leading the way in ensuring that vehicles are not only smart but also secure.
Future Directions in Automotive Cybersecurity
Emerging Threats
As vehicles become more connected, new threats are emerging. Cybercriminals are constantly finding ways to exploit vulnerabilities in vehicle systems. Some potential threats include:
- Increased API attacks: As vehicles rely more on APIs for communication, these become prime targets.
- Ransomware attacks: Hackers may hold vehicle systems hostage, demanding payment to restore functionality.
- Data breaches: Personal information stored in vehicles can be stolen if not properly secured.
Technological Advancements
The automotive industry is rapidly evolving, and so are the technologies used to combat cyber threats. Key advancements include:
- Artificial Intelligence: AI can help detect unusual patterns and potential threats in real-time.
- Blockchain: This technology can secure vehicle data and ensure its integrity.
- Advanced encryption: Stronger encryption methods are being developed to protect vehicle communications.
Industry Collaborations
Collaboration among industry players is crucial for enhancing cybersecurity. Some initiatives include:
- Partnerships between OEMs and cybersecurity firms: This helps in sharing knowledge and resources.
- Joint research projects: These can lead to innovative solutions for emerging threats.
- Standardisation efforts: Establishing common standards can help ensure all vehicles meet minimum security requirements.
The future of automotive cybersecurity relies on innovation and collaboration to stay ahead of threats. As vehicles become smarter, so must our security measures.
In summary, the automotive industry must remain vigilant and proactive in addressing the evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats. By focusing on emerging threats, leveraging technological advancements, and fostering industry collaborations, we can better protect our vehicles and the data they hold.
The Importance of Regulatory Compliance
UNECE WP29 Regulations
The UNECE WP29 regulations are crucial for ensuring that vehicles meet strict cybersecurity standards. These regulations require manufacturers to demonstrate that their vehicles have undergone thorough cybersecurity assessments. This means that before a vehicle can be sold in certain markets, it must pass specific tests to ensure it is safe from cyber threats.
ISO SEA 21434 Standards
The ISO SEA 21434 standards provide a framework for integrating cybersecurity into vehicle design and manufacturing. This standard helps manufacturers understand how to protect their vehicles from potential cyber attacks. By following these guidelines, companies can ensure that their vehicles are built with security in mind from the very start.
Impact on Manufacturers
Manufacturers must comply with these regulations to avoid penalties and maintain their reputation. Non-compliance can lead to:
- Fines and legal issues
- Loss of market access
- Damage to brand trust
Regulatory compliance is not just about following rules; it’s about ensuring the safety and security of every vehicle on the road.
In summary, adhering to these regulations is essential for manufacturers to protect their customers and their businesses. By prioritising compliance, they can build safer vehicles and foster trust in the automotive industry.
The Human Element in Automotive Cybersecurity
Training and Awareness
The human element in cybersecurity is crucial. People often make mistakes that can lead to security breaches. To combat this, training programmes should focus on:
- Understanding common cyber threats.
- Recognising phishing attempts.
- Safe online practises.
Role of Ethical Hackers
Ethical hackers play a vital role in identifying vulnerabilities before malicious hackers can exploit them. Their contributions include:
- Conducting penetration tests.
- Reporting security flaws.
- Suggesting improvements to security protocols.
Consumer Responsibility
Consumers also have a part to play in automotive cybersecurity. They should:
- Regularly update software in their vehicles.
- Be cautious when using third-party applications.
- Monitor for any unusual activity in their vehicle systems.
The human element in cybersecurity explores the role of human behaviour in cybersecurity risks. Psychological tactics used by cyber attackers can often exploit human weaknesses, making awareness and training essential for protection.
Final Thoughts on Automotive Cybersecurity
In conclusion, as cars become smarter and more connected, the need for strong cybersecurity is more important than ever. Protecting your vehicle from cyber threats is not just about technology; it’s about ensuring your safety and privacy. By following simple steps like keeping software updated, being careful with devices that connect to your car, and understanding how to secure your key fob, you can help keep your ride safe. As we move forward, staying informed about the latest security measures will be key to enjoying the benefits of modern vehicles while minimising risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is automotive cybersecurity?
Automotive cybersecurity is about protecting cars from cyber threats. It ensures that the software and systems in vehicles are safe from hackers.
Why is cybersecurity important for cars?
Cybersecurity is vital for cars because as vehicles become smarter and more connected, they are at risk of being hacked, which can endanger drivers and passengers.
What are common cyber threats to vehicles?
Common threats include hacking into the car’s systems, stealing personal information, and taking control of the vehicle remotely.
How can I protect my connected car?
To protect your car, regularly update its software, avoid using suspicious apps, and keep your key fob secure.
What are Electronic Control Units (ECUs)?
ECUs are small computers in cars that control various functions, like the engine and brakes. They need to be secured to prevent hacking.
What role do manufacturers play in cybersecurity?
Manufacturers are responsible for ensuring their vehicles are secure. They partner with cybersecurity firms and follow regulations to protect their cars.
What is V2V communication?
V2V, or vehicle-to-vehicle communication, allows cars to talk to each other to share information about traffic and safety, helping to prevent accidents.
What should I do if I notice unusual activity in my vehicle?
If you see anything strange, like unexpected alerts or changes in how your car works, contact a professional immediately to check for any security issues.
-
 Press Release4 days ago
Press Release4 days agoClinical Trials Market Set for Robust Growth, Driven by Drug Development Surge and Digital Innovation
-

 Press Release6 days ago
Press Release6 days agoBellarium ($BEL) Price Prediction: Could It Hit $5 by 2026?
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoIndustrial Boiler Market Expected to Surpass USD 24.4 Billion by 2035 Amid Growing Demand for Energy Efficiency and Industrialization
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoHow Managed IT Solutions Help Small Teams Compete at Enterprise Scale
-
 Press Release5 days ago
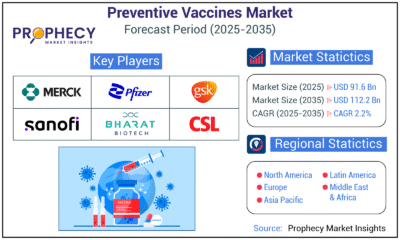
Press Release5 days agoPreventive Vaccines Market to Witness Strong Growth by 2035
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoGreen Bio Chemicals Market Poised for Sustainable Growth amidst Global Shift to Eco-Friendly Alternatives by 2035
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoFill-Finish Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Market Expected to Flourish Amid Biopharmaceutical Boom and Global Outsourcing Trend by 2035
-

 Press Release5 days ago
Press Release5 days agoPet Food Nutraceutical Market Set for Robust Expansion Amid Rising Demand for Pet Wellness by 2035